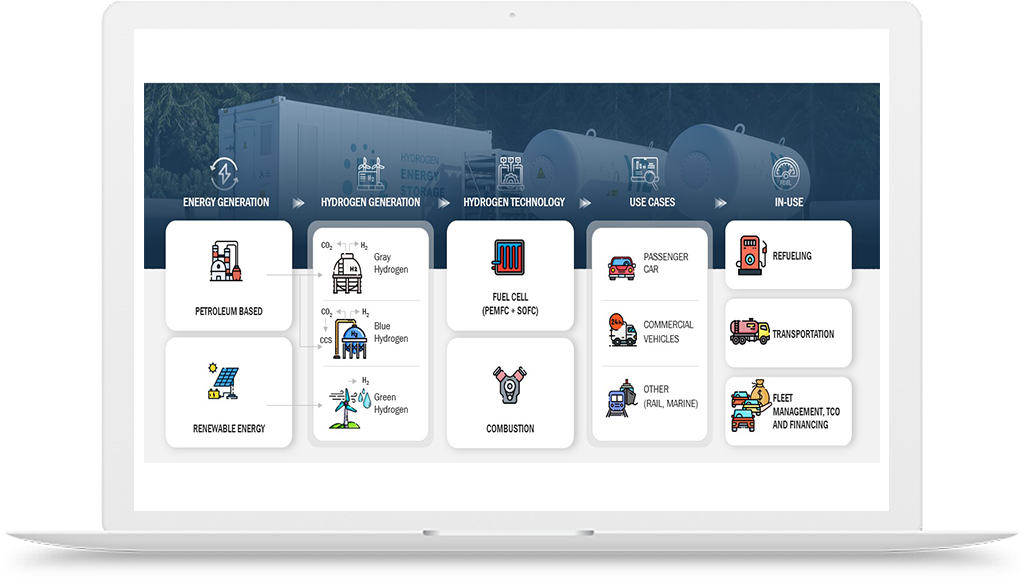
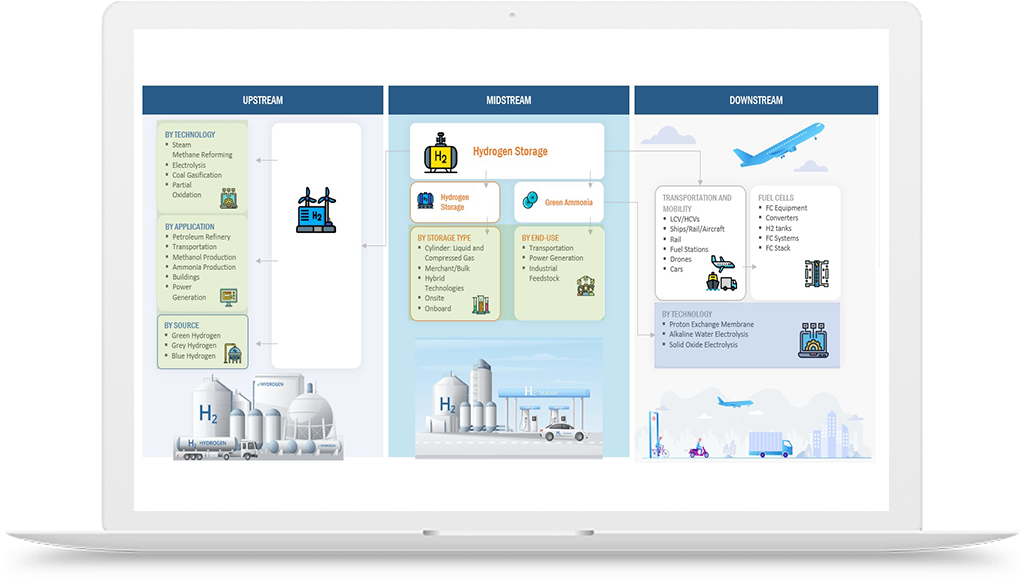
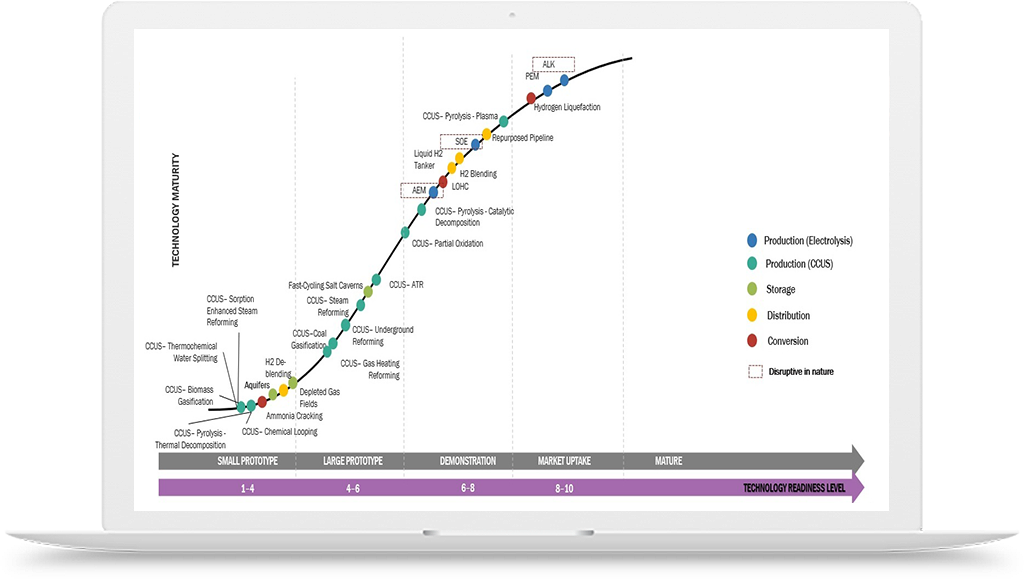
Hydrogen Application in Steel Production Industry
The use of green hydrogen in steelmaking processes is one way to decarbonize one of the most carbon-intensive industries. Hydrogen application in steel production industry is emerging as a game-changing solution.
Investigating the Hydrogen application in steel production industry entails using hydrogen as a reducing agent in blast furnaces, which can significantly lower carbon emissions and create a more environmentally friendly and sustainable steel manufacturing process.
The adoption of hydrogen application in steel production industry is a strategic move towards achieving net-zero emissions, with initiatives such as direct reduction using hydrogen and the development of hydrogen-based electric arc furnaces reshaping the landscape of steelmaking.
Hydrogen is a versatile and sustainable energy carrier that can be used in various industrial applications, including the production of steel. Steel is an essential material for many industries, and the use of hydrogen in its production offers several benefits, including:
The application of hydrogen in steel industry is a component of larger initiatives to accomplish sustainability objectives and decarbonize industrial processes. Even though there are still obstacles to overcome, continuing studies and pilot programs are advancing the use of hydrogen in steelmaking and opening the door for a more ecologically friendly future for the sector.
- Reduced carbon emissions: The steel industry is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases, and the use of hydrogen in steel production offers a way to reduce carbon emissions. Hydrogen can replace coal as a reducing agent in the blast furnace, resulting in lower carbon emissions and improved environmental performance.
- Improved energy efficiency: The use of hydrogen in steel product can ameliorate the energy effectiveness of the process. The use of hydrogen reduces the need for coking coal and increases the effectiveness of the steelmaking process, performing in lower energy consumption and reduced costs.
- Improved product quality: The quality of the finished steel can be raised by using hydrogen in the manufacturing process. By using hydrogen, the number of impurities in the steel can be decreased, producing products that are more reliable and of higher quality.
- Increased competitiveness: The use of hydrogen in steel production can increase the competitiveness of steel producers. Hydrogen-based steelmaking can reduce costs, improve energy efficiency and improve environmental performance, making it an attractive option for steelmakers looking to remain competitive in the market.
- Potential for revenue generation: The use of hydrogen in steel product offers the eventuality for profit generation through the trade of hydrogen by- product. Hydrogen produced during the steelmaking process can be captured and vended as a separate product, furnishing an fresh source of profit for steel directors.
- Direct Reduction of Iron Ore: In direct reduction processes, which turn iron ore into directly reduced iron (DRI) or sponge iron, hydrogen can be employed as a reducing agent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
How much hydrogen is used in steel making?
The amount of hydrogen used in steelmaking varies depending on the specific process and technology employed. In general, hydrogen usage can range from a few kilograms per ton of steel in conventional steelmaking to several hundred kilograms per ton in advanced hydrogen-based processes like direct reduction of iron ore or hydrogen plasma smelting.
How does hydrogen impact steel?
Hydrogen can have both positive and negative impacts on steel. While it can be used as a reducing agent in direct steelmaking processes, enabling lower carbon emissions, excessive hydrogen can lead to embrittlement and reduced mechanical properties in steel, making hydrogen control and management crucial in steel production.
How is hydrogen used in steel production?
Hydrogen is used in steel production primarily as a reducing agent in direct reduction processes, such as direct reduced iron (DRI) production, where it helps convert iron ore into metallic iron. Additionally, hydrogen can be used as a fuel in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) to provide heat for steel melting, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Why is hydrogen used in steel industry?
Hydrogen is used in the steel industry for its role as a clean and efficient reducing agent, enabling the direct reduction of iron ore and lowering carbon emissions in the steelmaking process. It offers an opportunity for decarbonization and transition towards more sustainable steel production methods.