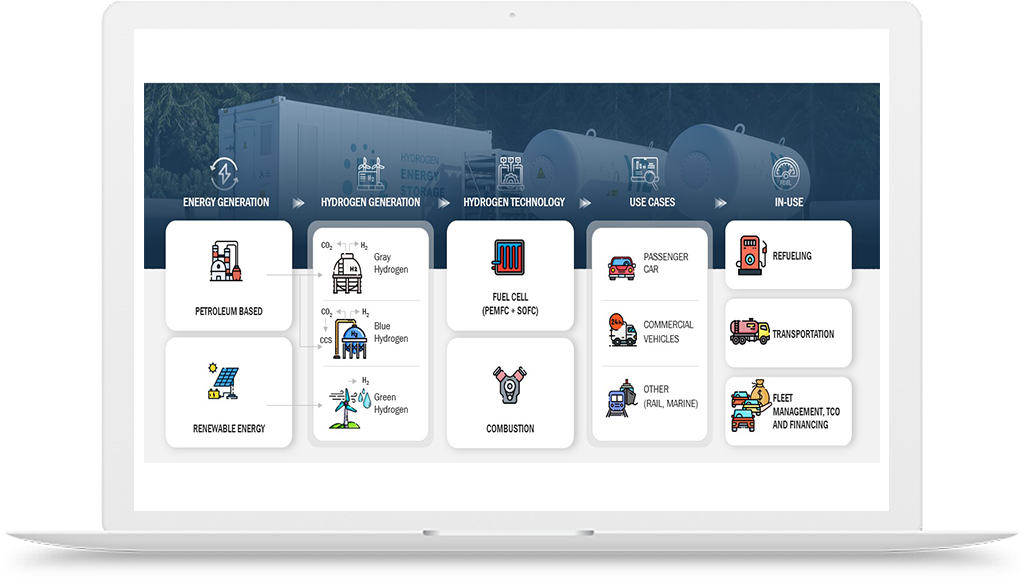
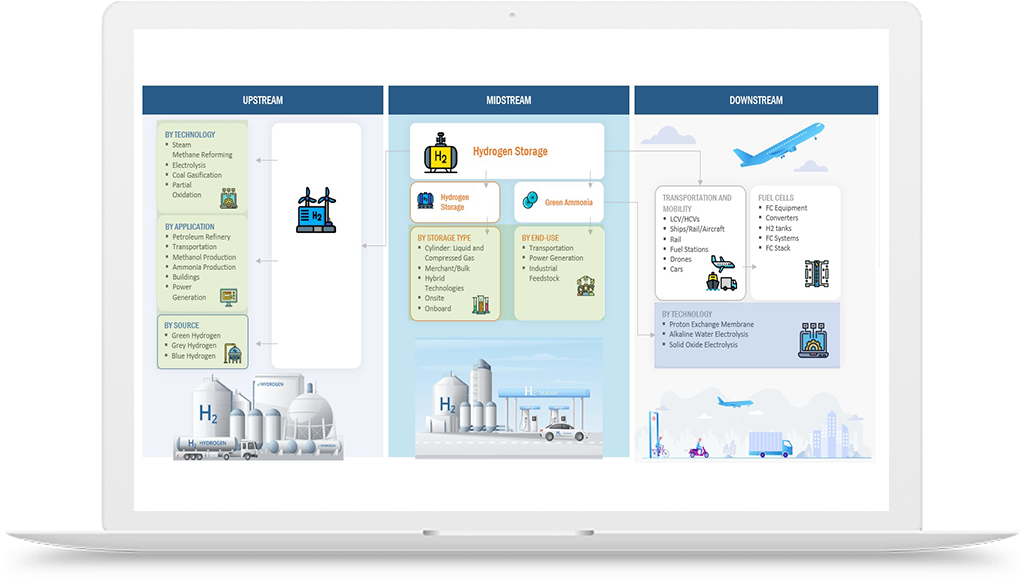
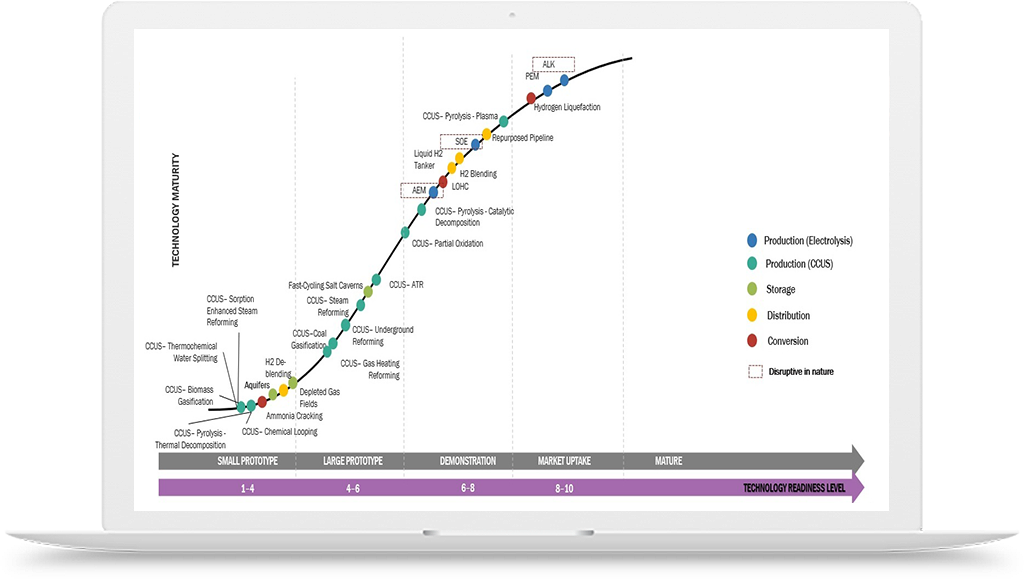
Hydrogen Application in Lab-grown Diamond Manufacturing Industry
Hydrogen is an essential element in the lab-grown diamond manufacturing process. In the conventional process, a mixture of hydrocarbon gas and hydrogen is heated to high temperatures, creating a plasma environment that allows diamond formation on a substrate. The hydrogen gas serves two important purposes in this process. Firstly, it acts as a reducing agent, which is necessary to maintain a suitable plasma environment for diamond growth. Secondly, it helps to prevent the formation of unwanted carbon species, such as graphite, which can interfere with diamond growth.
However, the use of hydrogen in lab-grown diamond manufacturing has also posed some challenges. For instance, the conventional process involves the use of high-pressure gas cylinders to store and deliver hydrogen gas to the manufacturing site. This can be expensive and pose safety risks during transportation and storage. Additionally, the use of hydrocarbon gas in the process can result in the emission of greenhouse gases and contribute to climate change.
To address these challenges, there have been efforts to develop alternative methods for lab-grown diamond manufacturing that use greener sources of hydrogen, such as water electrolysis. In this process, hydrogen gas is generated by splitting water molecules using electricity from renewable sources, such as wind or solar power. This process produces no greenhouse gas emissions and can be conducted on-site, reducing transportation costs and safety risks associated with hydrogen gas storage.
Another approach to greening the lab-grown diamond manufacturing process is to use alternative carbon sources, such as carbon dioxide captured from industrial emissions or direct air capture. By using renewable sources of hydrogen and alternative carbon sources, lab-grown diamond manufacturing can become a more sustainable and environmentally friendly process.