
Battery Swapping Market Size, Share & Analysis
Battery Swapping Market by Vehicle Type (2-wheeler, 3-wheeler, Passenger car, Commercial Vehicles), Operation (Manual, Automated), Service Type (Subscription, Pay-per-use), Application (Passenger, Commercial) & Region - Global Forecast to 2035




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The Battery Swapping market is projected to reach USD 22.72 billion by 2035, from USD 1.46 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 31.5%. The battery swapping market is primarily driven by the need to reduce EV downtime and improve fleet utilization, particularly in high-mileage applications such as two- and three-wheelers in India, China, and Southeast Asia. Operators and OEMs are adopting standardized, modular battery architectures to enable interoperability across vehicle platforms and brands, while government initiatives such as India’s draft battery swapping policy and China’s subsidies for swappable battery-equipped taxis and logistics fleets are accelerating infrastructure rollout. In addition, advancements in real-time battery monitoring, automated swapping robotics, and subscription-based energy-as-a-service models are making the business economically viable by lowering upfront vehicle costs and extending battery life through managed charging cycles.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
By RegionBy region, Asia Pacific holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market, supported by high EV adoption in densely populated urban areas. Strong government policies, expanding swapping networks, and the dominance of two- and three-wheeler EVs further strengthen the region’s leadership.
-
By Vehicle TypeThe two-wheeler segment dominates the battery swapping market as shared mobility operators and delivery fleets in countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam rapidly adopt electric scooters to cut downtime and operating costs. High vehicle utilization rates and dense urban deployment make battery swapping more viable for two-wheelers than for larger EVs, driving widespread network expansion by players like Gogoro, SUN Mobility, and Ola Electric.
-
By OperationThe automated segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market as advanced robotic systems streamline battery replacement with minimal human input, ensuring faster turnaround and higher reliability. Companies like NIO and AMPLE are leading this shift by deploying fully automated swap stations that use precision-guided robotics and cloud-based diagnostics to service vehicles efficiently, particularly in high-utilization fleet operations and densely populated urban zones.
-
By Service TypeBy service type, the subscription segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market due to its lower upfront costs and predictable monthly expenses for users. This model is increasingly preferred by fleet operators and daily commuters as it ensures continuous battery availability and easier cost management.
-
By ApplicationThe passenger segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market as rising adoption of electric scooters, motorcycles, and compact cars for personal mobility drives consistent demand for quick and convenient energy refueling. Urban consumers, especially in markets like China and India, favor battery swapping for its time efficiency over charging, with OEMs such as NIO and Ather Energy integrating swap-compatible models to enhance convenience and reduce range anxiety for daily commuters.
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPEThe battery swapping market is dominated by key players such as NIO (China), Gogoro (Taiwan), Ample (US), Sun Mobility (India), and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited. (China), among others. These companies have a global distribution network across Asia Pacific, North America, and Europe. They are vital in their domestic markets and explore geographic diversification alternatives to grow their businesses. They focus on increasing their market shares through expansions, investments, joint ventures, collaborations, and partnerships.
Battery swapping market growth is driven by the economics of maximizing asset utilization enabling fleet operators to decouple vehicle cost from battery cost while keeping vehicles in near-continuous operation. Further, Fleet operators in urban logistics and ride-hailing sectors are leveraging battery swapping to bypass long charging cycles and optimize operational efficiency. This shift is supported by partnerships between energy providers and mobility platforms such as NIO’s Power Swap network in China and Sun Mobility’s collaboration with Piaggio and Zypp Electric in India creating integrated ecosystems that enhance reliability and scalability.
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
The battery swapping market is experiencing strong momentum, driven by the surge in high-utilization EV segments such as two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and commercial fleets that require minimal downtime and predictable operating costs. Adoption is shifting toward interoperable, automated, and subscription-based swapping networks that reduce the burden of battery ownership while improving station economics. At the same time, OEM partnerships, government-backed standardization mandates, and advancements in modular battery designs are pushing ecosystem players to scale infrastructure rapidly and deploy new service-led business models for long-term competitiveness.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Rise in investments in battery swapping infrastructure by OEMs

-
Lower initial purchase cost of electric vehicles with battery swapping
Level
-
Lack of standardization of batteries used in different vehicles
-
Limited vehicle compatibility
Level
-
Introduction of innovative modular battery swapping solutions
Level
-
Battery Ownership and Business Model Challenges
-
Battery Degradation & Lifecycle Management
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Rise in investments in battery swapping infrastructure by OEMs
The surge in OEM-led investments toward dedicated battery swapping infrastructure is significantly accelerating market adoption. Companies like Gogoro, NIO, and Honda are deploying proprietary swapping stations and forming alliances with energy firms to secure battery supply chains and enable large-scale interoperability. These strategic investments not only enhance user accessibility and trust but also position OEMs to capture recurring revenue through subscription-based battery ownership models, strengthening long-term ecosystem control.
Restraint: Limited vehicle compatibility
Limited vehicle compatibility restricts the deployment of battery swapping solutions to only select EV models designed for standardized packs. This lack of interoperability discourages mass adoption among consumers and fleet operators. Thus, the battery swapping market faces slower expansion until broader standardization is achieved.
Opportunity: Introduction of innovative modular battery swapping solutions
The introduction of innovative modular battery swapping solutions enables compatibility across a wider range of EV models. These flexible designs simplify integration for automakers and reduce infrastructure complexity. As a result, modular systems open up strong growth opportunities for the battery swapping market by supporting scalable and efficient expansion.
Challenge: Battery degradation & lifecycle management
Battery degradation and lifecycle variability make it difficult to maintain consistent performance and fairness across swapped batteries. Operators must invest in advanced monitoring and management systems to track battery health and ensure safety. These complexities raise operational costs and create challenges for scaling the battery swapping market efficiently.
Battery Swapping Market: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) network for passenger EVs with fully automated swap stations in China and select EU markets. | Fast 3–5 min swaps, lower upfront EV price, extended battery lifecycle, grid-support energy operations. |
 |
Swappable battery ecosystem for e-scooters and lightweight EVs across Taiwan, India and Southeast Asia. | High network density and convenience, standardization reduces cost, accelerates micromobility electrification. |
 |
Battery swapping pilots for electric scooters integrated with its public charging network in India. | Higher vehicle uptime, reduced peak-load stress on charging infra, supports rapid adoption in dense cities. |
 |
Modular battery swapping for ride-hailing fleets and light commercial vehicles in the U.S., Europe and Japan. | Vehicle-agnostic solution, swaps in under 10 minutes, lower infrastructure CapEx due to modular micro-stations. |
 |
Interoperable swapping for 2- and 3-wheelers with pay-per-use subscription model in India. | Lower total cost of ownership for fleet operators, shared battery pool increases utilization, decarbonizes last-mile lo |
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The Battery Swapping ecosystem consists of vehicle manufacturers (NIO, Ola, Stellantis, Ather, Hero), infrastructure providers/battery swapping operators (Sun Mobility, Ample, Battery Smart, Esmito), Battery Manufacturers (CATL, LG Energy Solution, BYD, Samsung SDI, Panasonic Energy), Software provider (Bosch, Siemens, Huawei). The battery swapping ecosystem begins with battery manufacturers who design and supply standardized, swappable battery packs optimized for interoperability and fast charging outside the vehicle. Vehicle manufacturers integrate these modular battery formats into EVs, enabling seamless swapping as part of their energy delivery model. Battery swapping operators deploy and manage swapping stations, supported by software providers that deliver network connectivity, battery health monitoring, and payment integration. Together, this ecosystem ensures rapid energy replenishment, efficient lifecycle management of batteries, and a scalable alternative to plug-in charging, powering the growth of shared and commercial EV fleets in a circular mobility system.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Battery Swapping Market, By Vehicle Type
By vehicle type, the two-wheeler segment holds the largest share in the battery swapping market, supported by intense usage in urban mobility and last-mile delivery services. Swapping drastically reduces downtime for delivery riders, making it economically superior to plug-in charging. Additionally, widespread government incentives and strong participation from shared mobility operators are accelerating two-wheeler swapping infrastructure deployment.
Battery Swapping Market, By Service Type
By service type, the subscription segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market, as it eliminates high upfront battery costs and provides predictable monthly expenses for users. This model ensures guaranteed access to fully charged batteries, improving convenience and operational uptime for daily commuters and fleet operators. Growing adoption among shared mobility services and logistics fleets is further reinforcing subscription-led market dominance.
Battery Swapping Market, By Operation
By operation, the automated segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market, as it enables rapid, hands-free swaps that keep commercial EVs in continuous service. These stations integrate IoT and predictive analytics to pre-condition and assign optimal batteries, improving throughput and battery lifecycle economics. Automated swapping also reduces manual handling risks and supports high-density deployments in constrained urban environments, making it the preferred model for scalable networks.
Battery Swapping Market, By Application
By application, the passenger segment holds the largest market share in the battery swapping market, as private EV users demand quick turnarounds without being tied to home charging infrastructure. Swapping unlocks long-distance travel flexibility for compact EVs with smaller battery packs, reducing upfront vehicle cost while preserving range confidence. Additionally, automaker–infrastructure partnerships are expanding swapping-ready vehicle lineups, accelerating consumer adoption in densely populated cities where parking and charging access are limited.
REGION
Asia Pacific is expected to be the largest market for the battery swapping market during the forecast period
The battery swapping market in the Asia Pacific region is driven by rapid urbanization, increasing adoption of electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers, and strong government policies promoting EV infrastructure. Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are investing in battery swapping networks to address range anxiety and reduce charging time, making EV adoption more convenient. In China, in as of July 2025, Nio has launched its 1,000th highway battery swap station in China, finalising a network that links 550 cities. The company now operates 3,399 swap stations nationwide, alongside over 2,800 supercharging stations, as it continues domestic and European expansion. Government policies, such as subsidies for battery-swappable EVs and incentives for infrastructure development, further accelerate market growth.

Battery Swapping Market: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
In the Battery Swapping Market, Gogoro (Star) leads with a highly scalable and data-driven swapping ecosystem, powered by its smart modular battery platform, extensive station network, and strong synergies with connected two-wheeler partners across major Asian cities, ensuring maximum uptime and operational efficiency for users. Its dominance is further reinforced by global expansion and strategic OEM collaborations that accelerate standardization and market penetration. Sun Mobility (Emerging Leader) is rapidly advancing with its interoperable battery architecture, open energy network, and partnership-led deployment strategy, enabling cost-efficient swapping across multiple vehicle categories including two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and fleet applications, positioning it as a key challenger in fast-growing urban mobility markets.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 (Value) | USD 0.99 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2035 (Value) | USD 22.72 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 31.5% from 2025-2035 |
| Years Considered | 2021-2035 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2035 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion), Volume (Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | North America, Asia Pacific, and Europe |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: Battery Swapping Market REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

DELIVERED CUSTOMIZATIONS
We have successfully delivered the following deep-dive customizations:
| CLIENT REQUEST | CUSTOMIZATION DELIVERED | VALUE ADDS |
|---|---|---|
| Global Battery Swapping Operator / Mobility OEM |
|
|
| Competitive Mapping | Competitive mapping of key OEM investment trends and partnership strategies (e.g., Gogoro, NIO, Sun Mobility, Honda initiatives) | Guide OEM partnership and investment pathways to secure technology and market leadership |
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- April 2025 : CATL and Sinopec inked a cooperation framework agreement in Beijing. According to the agreement, both parties will commit to extensive and long-term strategic partnership in the hope of accomplishing a battery-swapping ecosystem across the whole nation, with no less than 500 battery swap stations complete in this year, and up to 10,000 ones in the long run.
- November 2025 : Ample (US) announced a USD 25 million investment from Mitsubishi Corporation (Japan). This strategic collaboration goes beyond just a financial investment, where Mitsubishi Corporation will support Ample's ongoing efforts to expand its battery-swapping business.
- Septmber 2024 : Nio (China) has signed an agreement with Suzhou Energy Group (China). The two companies will work together on charging and battery swap network construction, virtual power plant construction and operation, and the creation of zero-carbon stations.
- August 2024 : SUN Mobility (India) and Veera Vahana (India) showcased India’s first modular battery swapping technology for Heavy Commercial Vehicles at Prawaas 4.0 held in late August in Bangalore. SUN Mobility has tied relations with bus manufacturer Veera Vahana, based in Bangalore, in order to launch what is claimed being India’s first 10.5 meters battery swappable buses for intercity and mofussil (i.e. regional, suburban) routes.
- July 2024 : Gogoro (Taiwan) announced it has been certified to launch its battery swapping and Smartscooters in Singapore and plans to launch with its exclusive distribution partner, Cycle & Carriage (C&C) (Singapore). C&C also announced a partnership with Shell Recharge to launch battery swapping GoStations at Shell service stations in the Singapore market.
- COLUMN 'A' SHOULD BE IN TEXT FORMAT AND NOT DATE FORMAT :
Table of Contents

Methodology
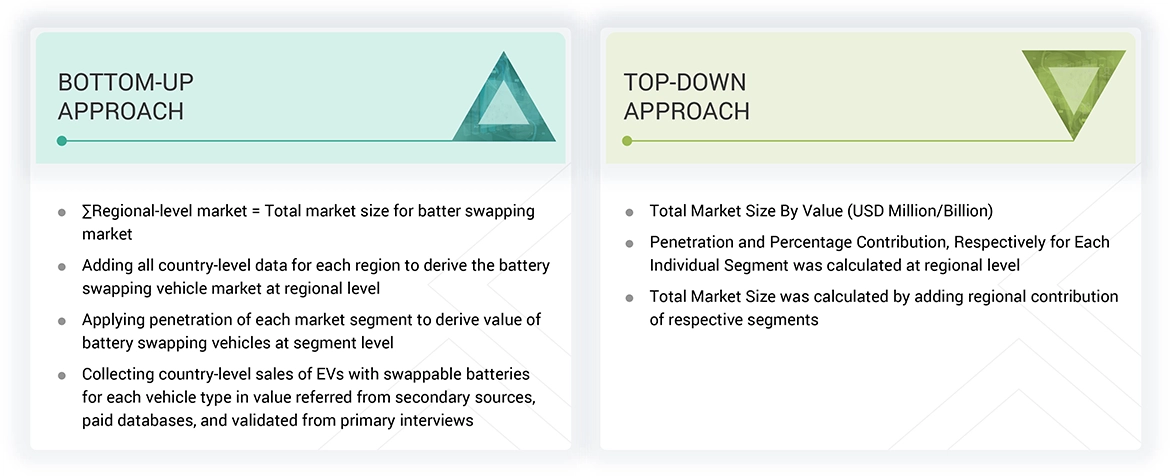
The study involved four major activities in estimating the current size of the battery swapping market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, the peer market, and the parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with the industry experts across value chains through primary research. The top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Thereafter, market breakdown and data triangulation processes were used to estimate the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
Secondary sources referred to for this research study include annual reports, press releases, investor presentations of companies, white papers, certified publications, and articles from recognized authors. Secondary research has been mainly used to obtain key information about the value chain of the industry, the total pool of key players, market classification, segmentation according to industry trends to the bottommost level, regional markets, and key developments from both market and application perspectives.
Primary Research
After understanding the battery swapping market scenario through secondary research, extensive primary research has been conducted. Primary interviews have been conducted with market experts from both demand- and supply-side players across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific. Approximately 20% of interviews have been conducted from the demand side, while 80% of primary interviews have been conducted from the supply side. The primary data has been collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews.
In the canvassing of primaries, various departments within organizations, such as sales and operations, have been covered to provide a holistic viewpoint in this report. Primary sources from the supply side include various industry experts, such as CXOs, vice presidents, directors from business development, marketing, product development/innovation teams, and related key executives from various key companies. Various battery swapping provider, industry associations, independent consultants/industry veterans, and key opinion leaders have also been interviewed.
After interacting with industry experts, brief sessions with highly experienced independent consultants have been conducted to reinforce the findings from the primaries. This, along with the opinions of in-house subject matter experts, has led to the findings described in this report.
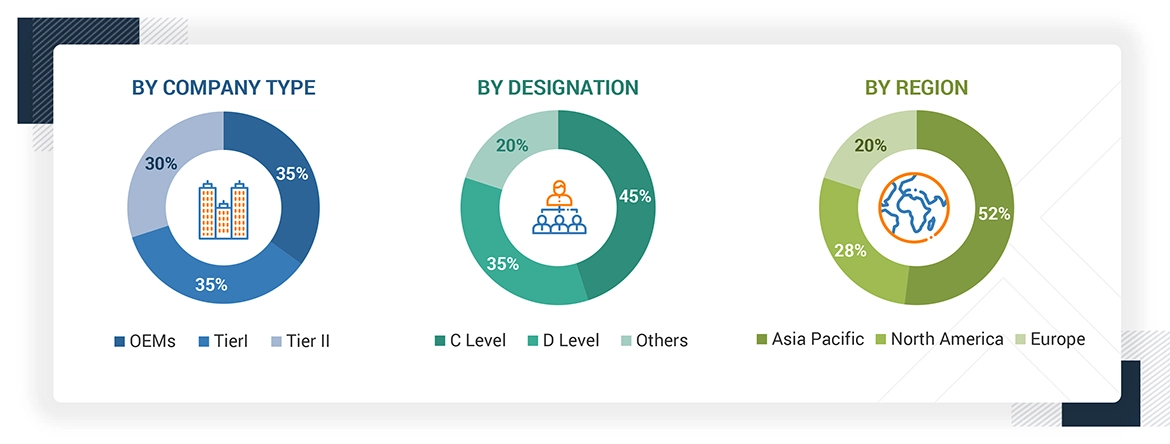
Note 1: Others include sales managers, marketing managers, and product managers.
Note 2: Tier 1 companies’ revenues are more than USD 10 billion; tier 2 companies’ revenues range between USD 1 and 10 billion; and tier 3 companies’ revenues range between USD 500 million and USD 1 billion.
Source: Industry Experts
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
- A detailed market estimation approach was followed to estimate and validate the value of the global battery swapping market and other dependent submarkets, as mentioned below:
- The market size was derived by using parameters such as sales of vehicles having swappable batteries
- Segment split was identified through primary and secondary research
- Key players in the global market were identified through secondary research, and their global market ranking was determined through primary and secondary research
- The research methodology included the study of the annual and quarterly financial reports & regulatory filings of major market players, as well as interviews with industry experts for detailed market insights
- All major penetration rates, percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns for the global battery swapping market were determined by using secondary sources and verified through primary sources
- All key macro indicators affecting the revenue growth of the market segments and subsegments were accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to get the validated and verified quantitative & qualitative data
- The gathered market data was consolidated and added with detailed inputs, analyzed, and presented in this report
Battery Swapping Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall size of the global market through the abovementioned methodology, this market was split into several segments and subsegments. The data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed, wherever applicable, to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact market value data for the key segments and subsegments. The extrapolated market data was triangulated by studying various macro indicators and regional trends from both the demand and supply-side participants.
Market Definition
According to Autotrader (UK), battery swapping involves switching out a depleted electric car battery with a fully charged one, rather than plugging it in to charge. The method usually takes under five minutes, which is a win for the electric vehicle (EV) community when compared to a 30-minute wait, or more, at a typical recharging station. The battery swapping process involves driving an EV to a battery swapping station and the station doing the rest of the work, including lifting the vehicle, removing the bolts for the chassis and battery, and then replacing the empty battery, all completely autonomously.
Battery swapping is an alternative to conventional charging and involves replacing depleted batteries with charged ones. Compared to charging, battery changing has three major benefits: it saves time, saves space, and saves money.
As of now, EV battery packs are not standardized, making them incompatible with a variety of car types, makes, and models. The interoperability of batteries will play a key role in the development and growth of the battery swapping market.
Stakeholders
- Battery Manufacturers
- Battery Swapping Operators
- Dealers & Distributors
- Government and Regulatory Authorities
- Automotive Manufacturers
- Battery Swapping Equipment Manufacturers
- Charging Station Providers
- Power Grid Operators
- Raw Material Suppliers
- Research and Consulting Associations
- Regional Vehicle Emission Regulatory Authorities
- Technology Companies
- Tier-I Component/System Manufacturers
Report Objectives
-
To define, segment, and forecast the size of the Battery Swapping market in terms of volume (thousand units) and value (USD million and USD thousand) based on the following categories
- To segment and forecast the market based on vehicle type (2-wheeler, 3-wheeler, Passenger Car, and Commercial vehicle)
- To segment and forecast the market based on application (passenger and commercial)
- To segment and forecast the market based on operation type (manual and automated)
- To segment and forecast the market based on service type (subscription and pay-per-use)
- Region (Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America)
- To identify and analyze key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing market growth
- To strategically analyze the market, considering individual growth trends, prospects, and their contribution to the total market
-
To study the following dynamics of the battery swapping market:
- Pricing Analysis
- Investment and Funding Scenario
- Supply Chain Analysis
- Ecosystem Analysis
- Technology Analysis
- HS Code/Trade Analysis
- Case Study Analysis
- Patent Analysis
- Regulatory Landscape
- Key Stakeholders and Buying Criteria
- Key Conferences and Events
- Impact of AI
- To strategically profile key players and comprehensively analyze their market share and core competencies
- To track and analyze competitive developments, such as product launches/developments, deals, expansion, and other developments carried out by key players
Available Customizations
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations in line with the company’s specific needs.
- Battery Swapping Market, By Operation Type at Country Level
- Battery Swapping Market, By Service Type at Country Level
Company Profile
- Profiling of Additional Market Players (Up to 3)
Key Questions Addressed by the Report
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the Battery Swapping Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation











Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Battery Swapping Market