
Nuclear Power Market Size, Share, Growth, Analysis
Nuclear Power Market by Plant Lifecycle Stage (EPC, Decommissioning, Operation & Maintenance), Type (Nuclear Power Plant, SMR), Application (Power Generation, Desalination, Industrial), Connectivity, Capacity, and Region - Global Forecast to 2029




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The nuclear power market is forecasted to reach USD 44.71 billion by 2029 from an estimated USD 38.84 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 2.9% during the forecast period (2024-2029).Nuclear power plants are designed to be very long-lived; usually, they last about 40 to 60 years. On top of that, some even have life extension programs. This would allow utilities to spread out the high costs of construction over several decades, thus making nuclear power a stable and financially viable source over the long term. Importing oil, gas, or coal has no meaning for countries as the shift to nuclear energy, this raises a great opportunity to improve energy independence. Nations can minimize their vulnerability to international fuel price fluctuations, geopolitical crises, or other disruptions to supply chains that affect fossil fuel markets if they rely on domestically produced nuclear energy
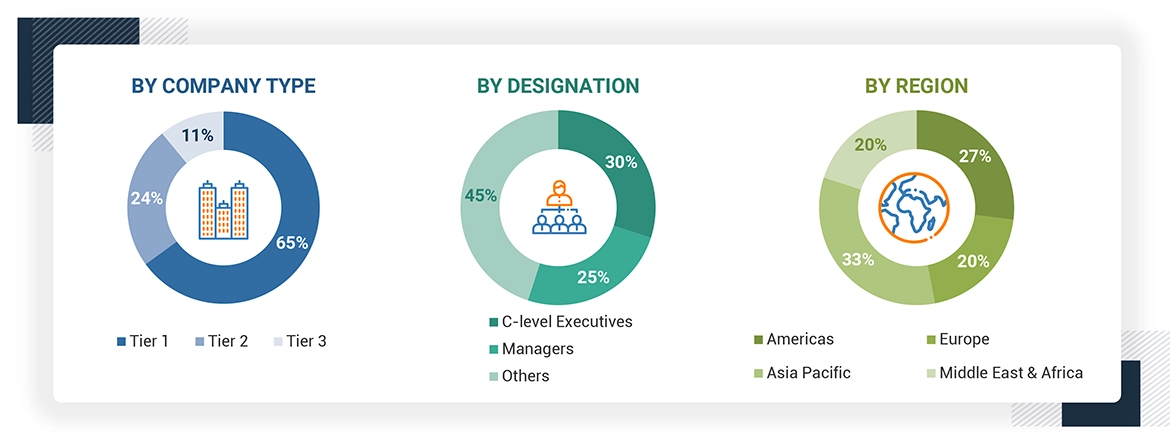
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
BY REGIONThe Asia Pacific nuclear power market is estimated to dominate with a share of 56.4% in 2024.
-
BY CAPACITYBy Capacity, the Small (Leass than 500 MW) segment is anticipated to record a CAGR of 3.0% between 2024 and 2029.
-
BY TYPEBy Type, the Nuclear Power Plants segment is the largest market in 2023.
-
BY CONNECTIVITYBy Connectivity, the Off-grid segment is expected to register the highest growth in the forecasted period.
-
BY PLANT LIFECYCLE STAGEBy Plant Lifecycle Stage, the Decommissioning segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 3.8% in the forescasted period.
-
BY APPLICATIONBy application, Power Generation Segment is to be the largest market in 2029.
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPEThe State Atomic Energy Corporation ROSATOM, EDF, MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD., AtkinsRéalis, and Westinghouse Electric Company LLC. have been identified as the star leaders in the nuclear power market, backed by their robust & strong global presence, and accelerating their adoption among utilities, industries, and large-scale nuclear projects.
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPESeaborg Technologies, newcleo, Thorcon CC BY-SA, ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR, and Last Energy, Inc. have distinguished themselves among SMEs and Startups due to their strong product portfolio and business strategy.
The nuclear power market is gaining renewed momentum as countries seek reliable, low-carbon electricity to support rising demand, grid stability, and long-term decarbonization goals. Nuclear power plants provide continuous, dependable baseload generation that complements variable renewable energy sources and enhances overall system resilience. Growing concerns around energy security and fuel supply volatility are also driving interest in nuclear energy, as it reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels and offers long operating lifetimes with stable fuel costs. At the same time, government support, policy recognition of nuclear as a clean energy source, and advancements in reactor technologies are improving project viability, reinforcing nuclear power’s role as a strategic and reliable pillar of future energy systems.
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
Growing demand for reliable, low-carbon baseload electricity and improved energy security is expected to drive the nuclear power market. Furthermore, increasing adoption of life-extension programs, small modular reactors, and advanced nuclear technologies to support net-zero targets, stabilize renewable-heavy grids, and reduce long-term power supply risks is projected to create sustained growth opportunities across the nuclear power sector.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Increasing nuclear power projects

-
Surging adoption of nuclear technology
Level
-
Requirement for high initial investment
-
Nuclear waste management concerns
Level
-
Significant focus on modernizing energy infrastructure
-
Strengthening global partnerships to advance nuclear power
Level
-
Complex decommissioning process and high cost of modification
-
Risks associated with nuclear proliferation
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Increasing nuclear power projects
The main dirver is Increasing nuclear power projects with countries catching on to the fact that nuclear energy can help deal with the challenges of energy security and climate change, more demand for clean energy propels the nuclear power market. Nuclear Energy Project in the World According to projections by the International Atomic Energy Agency, the global nuclear capacity has upwardly revised; by 2050, it points to an increase of 25% above previously done projections that were based on estimations from 2020. Several countries have begun to understand and recognize its position as an important solution to many problems concerning energy security and climate change. In the light of the increasing worldwide consensus of nations toward nuclear power as a low-carbon, reliable source of energy to be used in the attainment of decarbonization goals and complementing energy security in response to volatile fossil fuel prices and geopolitical tensions. Nuclear power delivers about 10 percent of the electricity in the world and as of July 2024, about 20 percent of Europe, according to the World Nuclear Association. This production is important in curbing carbon emissions since, traditionally, it is one of the biggest sources of carbon-free electricity.
Restraints: Requirement for high initial investment
Nuclear power plants are among the most capital-intensive sources of electricity. This means high initial capital and maintenance costs. Capital costs, including financing (at a high discount rate), for nuclear power for a 2,200 MWe plant range between USD 3,000 and USD 4,000 per kilowatt. LCOE varies from USD 129/MWh to USD 198/MWh, considering specific factors like a particular location, the regulatory environment applicable at that location, and a specific technology. This immense amount of spending is primarily attributed to its complex engineering and safety systems; in fact, such long lifetimes, up to 60 years, can easily compromise its safe operation. The maintenance costs of nuclear power plants are relatively lower compared to their initial capital costs. Once operational, these facilities usually have low and stable operational costs. However, maintenance would include rigorous safety checks and regulatory compliance measures that may still incur significant costs over time. Decommissioning at the end of a plant's life cycle also adds to the financial burden, estimated to be around 9 to 15% of the initial capital cost. Another critical factor that determines the economics of nuclear power is the financing structure.
Opportunities: Significant focus on modernizing energy infrastructure
Nuclear-renewable hybrid energy systems (NRHES) are a new way of combining nuclear power with renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower to provide the greatest strength for both. Such systems go a long way in solving some of the key issues in the energy transition, particularly regarding reliability, sustainability, and decarbonization across sectors. The system can offer constant baseload power to supplement the variability of the renewable source, whose generation varies with the weather. Coupling these sources of energy, NRHES assures a grid with a constant electricity supply regardless of low renewable generation time. Hybrid systems can supplement these sectors, which include industrial processes, desalination, and hydrogen production to add low-carbon energy to electricity grids. Small modular reactors are core to the hybrid systems. This serves as a low-carbon replacement to aging fossil fuel plants while incorporating some 50 concepts under development worldwide for small modular reactors, which are designed suitable both for electric and non-electric applications, heating included with water desalination so as to stabilize grids at a lesser cost of a low carbon transition. Other nuclear-renewable systems are being ventured at Idaho National Laboratory (INL) to power hydrogen production integrated with the intermittent usage of the resources.
Challenges: Complex decommissioning process and high cost of modification
Decommissioning and upgrading are serious problems facing the nuclear power market. Decommissioning is defined as decontamination followed by the step-by-step removal of a nuclear plant by an owner who intends to retire it. Decommissioning involves defueling, followed by coolant removal; the NRC defines it, however, as starting only when such elements are removed from a decommissioned plant. Its process ends with license revocation after verification of successful decontamination and waste removal. According to the IAEA, the decommissioning and waste management of a nuclear reactor will cost about USD 500 million to USD 2 billion by April 2023. The decommissioning of gas-cooled graphite-moderated reactors is costlier than that of pressurized or boiling water reactors as they are larger and more complicated in size. For large fuel cycle facilities such as spent fuel reprocessors, decommissioning costs come in the range of about 4 billion USD to be completed over more than 30 years. It will cost over 20 million USD and take between 5 to 10 years to decommission a research reactor that has a thermal output of 10 megawatts; this would depend upon other factors, such as the size and purpose of the reactor and its operating history.
NUCLEAR POWER MARKET SIZE, SHARE, GROWTH, ANALYSIS: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
Qinshan Nuclear Power Plant operates multiple nuclear reactor units to provide stable, low-carbon electricity while maintaining high safety and operational reliability. The plant focuses on meeting regulatory standards, extending reactor lifetimes, and ensuring consistent power generation to support China’s electricity needs. | The plant delivers reliable baseload power with low emissions, supports long-term energy security, and contributes to carbon reduction through sustained nuclear generation. |
 |
ORLEN Synthos Green Energy is developing small modular reactor projects in Poland to support the transition away from coal and provide reliable, low-carbon electricity, particularly for industrial users. The initiative focuses on replacing aging coal assets and meeting future energy demand. | The SMR projects are expected to reduce coal dependence, lower emissions, and improve energy security while supporting Poland’s long-term decarbonization goals. |
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The nuclear power market ecosystem includes component and equipment manufacturers, engineering–procurement construction (EPC) players, operation and maintenance service providers, waste management and decommissioning specialists, reactor owners and operators, and end users working together to support reliable nuclear power generation. Component and equipment manufacturers such as SINOMACH, GE Hitachi, and Godrej supply critical nuclear-grade systems, turbines, and reactor components. EPC players including Bechtel and Fluor manage plant design, construction, and project execution. Operation and maintenance providers such as Southern Nuclear, Exelon, EDF, and CGN ensure safe and efficient plant operations. Waste management and decommissioning service providers including Veolia, Bechtel, Holtec International, and EnergySolutions handle spent fuel, radioactive waste, and plant decommissioning. Reactor owners and operators such as Westinghouse, GE Hitachi, Rosatom, and Framatome support reactor technology deployment, while end users including NTPC, Tata Power, Adani Power, and ACWA Power utilize nuclear energy to deliver stable, low-carbon electricity.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Nuclear power market, By Connectivity
Off-grid segment to grow at highest CAGR during forecast period. This nuclear systems grant regular access to energy sources in remote and isolated sites where grid infrastructure is out of reach or unreliable. Through these systems, electricity will be supplied to vital services: health, education, and communication service, thus improving living conditions. Microreactors would highly thrive in such environments in the light of sustainable, constant power but without necessarily requiring huge infrastructural setups to be supported, especially in their deployment towards rural electrification and industries. Off-grid nuclear systems offer the possibility of being independent at the community level, industrial level, or country level because they do not depend on the central grid or on imports for sources of their energy. In the event of a failure in the grid or geopolitical instability, these systems will provide a continuous and self-sustaining energy supply. It is highly beneficial for remote military bases, research stations, or island communities because they require reliable energy solutions to continue their operations and survival. Nuclear off-grid solutions provide reliable power in disaster-prone regions or in areas where there are frequent grid failures. Such systems can operate completely off the central grid and can ensure a continuous supply during emergencies
Nuclear power market, By Type
Small nuclear reactors to be fastest-growing segment during forecast period. Many governments are promoting small nuclear reactors through policy frameworks, funding programs, and research initiatives. Such efforts are aimed at accelerating the deployment of SNRs within clean energy strategies. Innovating policies, financial incentives, investments, and favorable conditions allow for the widespread use of small nuclear technologies. SNRs will be the ideal technology in remote areas where infrastructures are few. A reliable source of power for a remote area would be provided. Their compact size makes them usable in remote locations, from islands to mining and military bases, where large-scale reactors are not feasible to deploy. This guarantees electricity access with stable, low-carbon origins in areas where the grid connection is difficult, thus minimizing reliance on expensive, polluting diesel generators. Modularity also enables the deployment of small nuclear reactors, in which the deployment can grow by adding modules as requirements increase. It thus fits regions experiencing fluctuating or gradually rising energy demands. Modular design facilitates phased deployment and helps reduce higher upfront costs with efficient resource utilization. Also, advanced small reactors feature innovative safety technologies such as passive cooling systems and integrated containment designs. Such features reduce the chance of accidents along with operational intricacy and make SNRs safer and more acceptable in the eyes of the public and regulatory bodies
Nuclear power market, By Capacity
The Large (Above 1,000) segment, by capacity, is expected to be the largest segment in the nuclear power market during the forecast period Large reactors generate a lot of electricity, hence achieving economies of scale. Their high output helps to cover increasing energy demand in a much better way that brings the economies in the long term. The plants become favorites because they provide a constant and stable power supply for big industrial sectors and urban centers. Moreover, Large nuclear reactors create stable baseload power, hence stabilizing the grid, primarily because of the growing integration of renewables in countries. This helps ensure a stable, consistent supply of energy, and, as such, large reactors are capable of supplying a long power system demanding a constant generation of electricity
Nuclear power market, By Plant Lifecycle Stage
The Nuclear Power Plants segment of the market is expected to hold the major share during the forecast period. Nuclear power is based on a well-established technology developed over many decades with proven reliability for large-scale generation. This mature infrastructure, coupled with continuing advances in safety, lends nuclear power plants to be a very reliable source of energy for countries seeking stable, continuous power production
Nuclear power market, By Application
Power Generation by Application is expected to be the largest segment in the nuclear power market during the forecast period. Nuclear power plants produce enormous amounts of electricity uninterruptedly and thus are the choice option for increased energy production based on increasing urbanization, industrialization, and technological development. Their baseload capability to produce stability and reliability in power is essential, especially in emerging economies where electricity consumption keeps rising. Since the energy generation from wind and sun is intermittent, a high output by nuclear power ensures constant energy generation while reducing dependence on fossil fuel as energy needs expand more globally
REGION
Asia Pacific is the largest region in the nuclear power market
The Asia Pacific is the largest in power nuclear market due to growth factors include increasing demand, fast-paced urbanization, and aggressive decarbonization agendas. China, India, South Korea, and Japan have led by using nuclear energy to answer to power shortages and lower their greenhouse gas emissions. China is currently leading the pack for the region in the area of investments in advanced nuclear technologies, including SMRs, with the purpose of diversifying a clean energy portfolio that will eventually aim at achieving carbon neutrality. To that effect, India will focus on nuclear power meeting electricity needs that keep increasing even as it remains committed to climate change mitigation. Nuclear expansion is fueled further by support from the government and international cooperation. For example, Japan has refocused on energy security by restarting reactors and promoting advanced technologies in its net-zero strategy. South Korea is building its nuclear sector at home but then opening up the rest of the world to the reactor design and export expertise of the country. Overall, the Asia Pacific nuclear power market is growing on account of strong government policies, technological advancements, and international partnerships.

NUCLEAR POWER MARKET SIZE, SHARE, GROWTH, ANALYSIS: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
Rosatom is a key participant in the global nuclear power market, leveraging its integrated capabilities across reactor design, nuclear fuel supply, engineering, construction, and lifecycle services to support large-scale nuclear power projects. The company provides solutions spanning Generation III+ reactors, small modular reactors, nuclear fuel fabrication, and plant operation and maintenance, enabling reliable, low-carbon baseload electricity generation. Rosatom’s focus on safety, standardized reactor designs, and long-term service agreements supports cost certainty, operational reliability, and extended plant lifetimes. Strategic partnerships with governments, utilities, and international stakeholders strengthen its role in advancing nuclear energy deployment, particularly in regions prioritizing energy security and decarbonization. With rising interest in nuclear power to support net-zero targets and grid stability, Rosatom’s comprehensive technology portfolio and global project experience position it as a significant contributor to the expansion of nuclear power infrastructure worldwide.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
- The State Atomic Energy Corporation ROSATOM (Russia)
- EDF (France)
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. (Japan)
- AtkinsRéalis (Canada)
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC. (US)
- Ontario Power Generation Inc. (Canada)
- Bilfinger SE (Germany)
- Southern Company (US)
- Enel Spa (Italy)
- Holtec International (US)
- Bechtel Corporation (US)
- KEPCO (South Korea)
- Duke Energy Corporation (US)
- Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (Japan)
- Rolls-Royce plc (UK)
- ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR (US)
- Seaborg Technologies (Denmark)
- TERRAPOWER LLC (US)
- Orana (France)
- Thorcon CC BY-SA (Singapore)
- ŠKODA JS a.s. (Czech Republic)
- Last Energy, Inc. (US)
- newcleo (Paris)
- Vattenfall AB (Sweden)
- China National Nuclear Corporation (China)
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 (Value) | USD 34.02 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2030 (Value) | USD 44.71 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 2.9% from 2024-2030 |
| Years Considered | 2020–2029 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024–2029 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | Americas, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Middle East & Africa |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: NUCLEAR POWER MARKET SIZE, SHARE, GROWTH, ANALYSIS REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- September 2024 : France's Nuclear Safety Authority approved EDF (France) to begin the divergence process at the Flamanville 3 reactor, marking the start of its first nuclear reaction. After months of testing, the reactor will generate a low-power stable nuclear reaction at 0.2% capacity, with plans to gradually increase power. Once it reaches 25%, the reactor will be connected to the electricity grid by autumn 2024, followed by further testing and power ramp-up.
- May 2024 : Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (UAE) and KEPCO (South Korea) signed a memorandum of understanding to bolster research and investment opportunities in nuclear energy in third countries.
- March 2024 : Enel Spa (Italy) and Ansaldo Nucleare (Italy) signed an agreement to examine and evaluate new technologies and business models for the generation of nuclear energy, such as small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced modular reactors (AMRs), and their industrial applicability. These are state-of-the-art innovative reactors, some of which are still under development, which will potentially enable electricity generation from nuclear sources sustainably and economically, ensuring a high degree of versatility and flexibility during operation. The agreement aims to explore the prospects of these two cutting-edge technologies, analyzing their opportunities from an industrial point of view.
- January 2024 : Capital Power (Canada) and Ontario Power Generation (Canada) entered into an agreement to jointly assess the development and deployment of grid-scale small modular reactors (SMRs) to provide clean, reliable nuclear energy for Alberta. The two companies will examine the feasibility of developing SMRs in Alberta through the agreement, including possible ownership and operating structures. SMRs are being pursued by jurisdictions in Canada and worldwide to power the growing demand for clean electricity and energy security.
- June 2022 : Bechtel Corporation (US), a trusted engineering, construction, and project management partnered with the global nuclear industry, signed a memorandum of understanding with Toshiba America Energy Systems (US) and Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions (US) to pursue a new civil nuclear power plant project in Poland
Table of Contents

Methodology
This research study involves the use of extensive secondary sources, directories, and databases, such as Hoovers, Bloomberg L.P., Factiva, ICIS, and OneSource, to identify and collect information useful for this technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the global nuclear power market. Primary sources are mainly industry experts from core and related industries, preferred suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, service providers, and organizations related to all segments of the value chain of this industry. In-depth interviews were conducted with various primary respondents, including key industry participants, subject matter experts, C-level executives of key market players, and industry consultants, among other experts, to obtain and verify critical qualitative and quantitative information as well as assess growth prospects of the market.
Secondary Research
The secondary sources for this research study include annual reports, press releases, investor presentations of companies, white papers, certified publications, articles by recognized authors, and databases of various companies and associations. Secondary research was mainly used to obtain key information about the supply chain and identify the key players offering nuclear power, market classification, and segmentation according to the offerings of the leading players, along with the industry trends to the bottom-most level, regional markets, and key developments from both, market- and technology oriented perspectives.
Primary Research
In the primary research process, various sources from the supply and demand sides were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information for this report. Primary sources from the supply side include industry experts such as chief executive officers (CEOs), vice presidents (VPs), marketing directors, and related key executives from various companies and organizations operating in the nuclear power market.
In the complete market engineering process, the top-down and bottom-up approaches and several data triangulation methods were extensively used to perform the market size estimations and forecasts for all segments and subsegments listed in this report. Extensive qualitative and quantitative analyses were conducted to complete the market engineering process and list key information/insights throughout the report.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both the top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the nuclear power market and its dependent submarkets. The key players in the market were identified through secondary research, and their market share in the respective regions was obtained through primary and secondary research. The research methodology includes the study of the annual and financial reports of top market players and interviews with industry experts, such as chief executive officers, vice presidents, directors, sales managers, and marketing executives, for key quantitative and qualitative insights related to the market.
Nuclear Power Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach

Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size from the estimation process explained above, the total market has been split into several segments and sub-segments. Data triangulation and market breakdown procedures have been used wherever applicable to complete the overall market engineering process and to arrive at the exact statistics for all segments and sub-segments. The data has been triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides. The market has been validated using both the top-down and bottom-up approaches. Then, it was verified through primary interviews. Hence, for every data segment, there are three sources—the top-down approach, the bottom-up approach, and expert interviews. When the values arrived at from the three points matched, the data was assumed to be correct.
Market Definition
Nuclear power is produced through the energy released during nuclear fission. In nuclear power plants, electricity is generated by harnessing this process, where heavy atoms such as uranium-235 split when struck by a neutron. This splitting triggers a chain reaction, releasing more neutrons and significant heat. The heat is then used to produce steam, which drives turbines connected to generators, ultimately producing electricity.
The nuclear power market represents the sum of year-on-year installation of nuclear reactor capacities by global companies and electricity generated by nuclear power plants each year, covering the entire plant lifecycle stages. In this study, the sum of the year-on-year cost of decommissioning and maintenance & operation services has been considered. Additionally, the study also includes the revenues of the companies that are considered during the study period. In EPC segment, the equipment cost is also considered.
Stakeholders
- Companies in the energy & power sector
- Government and research organizations
- Investment banks
- Engineering, Procurement, and Construction companies
- Decommissioning service providers
- Maintenance & Operations services providers
- Nuclear power plant owners/operators
- Power and energy associations
- Nuclear power plant equipment support service providers
- Manufacturers of nuclear power plant equipment
- Nuclear power plant equipment component manufacturers
- Power generation companies
- Heavy industries
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, and forecast the nuclear power market based on type, connectivity, capacity, plant lifecycle stage, application, and region in terms of value
- To forecast the market by type and region in terms of volume
- To describe and forecast the market for four key regions: Americas, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, along with their country-level market sizes in terms of value
- To provide detailed information on the major factors influencing the growth of the market (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges)
- To strategically analyze the micromarkets1 with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions to the overall market size
- To provide market dynamics, trends/disruptions impacting customer business, supply chain analysis, ecosystem analysis, case study analysis, investment and funding scenario, patent analysis, trade analysis, technology analysis, key conferences & events, regulatory landscape, pricing analysis, key stakeholders and buying criteria, global macroeconomic outlook for nuclear power market, Porter’s five forces analysis, pertaining to the nuclear power plant market
- To benchmark players within the market using the company evaluation matrix, which analyzes market players on various parameters within the broad categories of business and product strategies
- To compare key market players with respect to their market share, product specifications, and applications
- To strategically profile key players and comprehensively analyze their market rankings and core competencies2
- To analyze competitive developments, such as contracts & agreements, investments & expansions, mergers & acquisitions, partnerships, and collaborations, in the market
- To study the impact of AI/Gen AI on the market under study, along with the global macroeconomic outlook
Note: 1. Micromarkets are defined as the further segments and subsegments of the nuclear power market included in the report.
2. Core competencies of companies are captured in terms of their key developments and product portfolios, as well as key strategies adopted to sustain their position in the market.
Available Customizations
MarketsandMarkets offers customizations according to the specific needs of the companies with the given market data.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Regional Analysis
- Further breakdown of the nuclear power market, by country
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to five)
Key Questions Addressed by the Report
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the Nuclear Power Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation














Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Nuclear Power Market