Space Outlook 2035: Market Overview (Ecosystem, Macroeconomics, Regulatory, Programs, Expenditure, Alliances, Dynamics), Industry Trends (Technologies, Use Cases, Maturity Curve), Market Segments (Satellites and Ground Stations), Customer Insights (Operators, OEMs, Shifts, initiatives, Business Models, Market Position), Competitive Landscape (Competitors, Partners, Evaluation Matrix, Key Profiles) and Future Opportunities (Future Landscape, Technology Roadmap, Major Projects, Top Opportunities)
The space industry is undergoing a transformative shift, with advancements in technology, increasing commercialization, and greater government-private sector collaboration. By 2035, space exploration, satellite communications, and commercial space travel will become more accessible, cost-efficient, and integrated into global economic and security frameworks. This article examines the market outlook, key industry trends, customer insights, competitive landscape, and future opportunities in space exploration and commercialization.
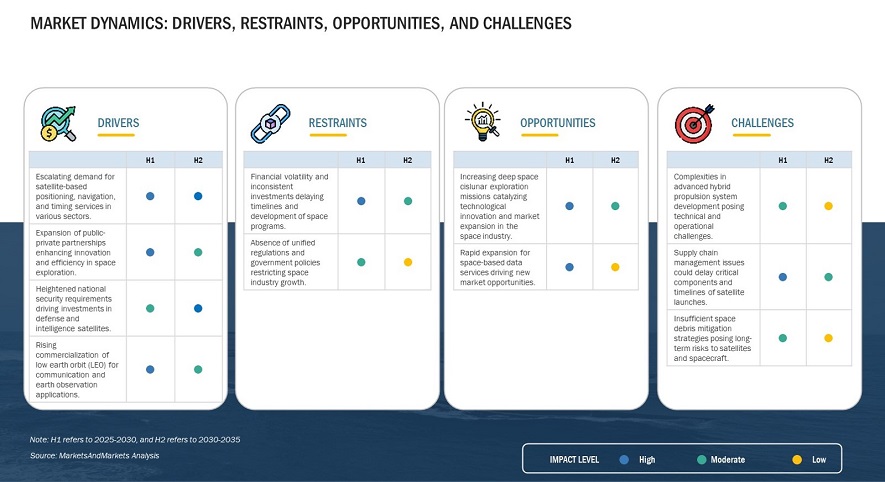
Market Overview
By 2035, the global space economy is projected to surpass $1.5 trillion, driven by increased investments in satellite technology, space tourism, interplanetary exploration, and defense applications. The space market is broadly segmented into:
- Satellite Industry – Communications, Earth observation, and navigation satellites will dominate the market.
- Space Exploration and Colonization – Lunar and Mars missions will expand, with a focus on resource utilization and human settlement.
- Commercial Space Travel – Space tourism and private spaceflights will become mainstream.
- Defense and Security – Increased focus on space-based surveillance, cybersecurity, and military applications.
- In-Orbit Services – Refueling, debris removal, and satellite servicing will emerge as critical industry segments.
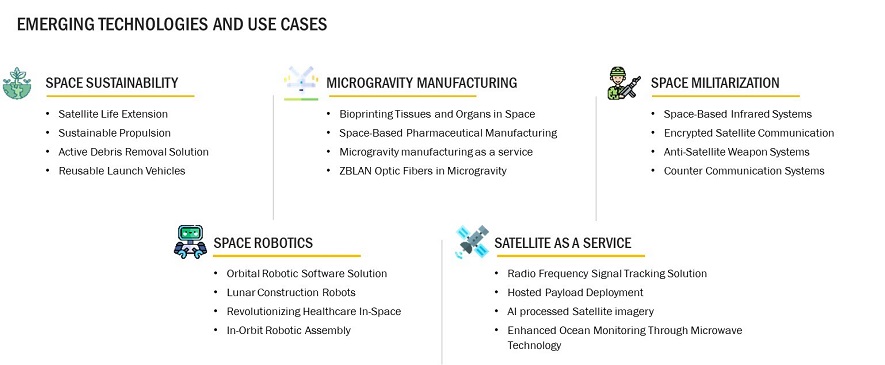
Industry Trends
- Reusable Rocket Technology – Reducing launch costs through reusable rockets will be a game-changer for space logistics.
- Space Mining and Resource Utilization – Mining asteroids and lunar resources will support deep-space missions and commercial activities.
- Satellite Mega-Constellations – Companies like SpaceX, Amazon, and OneWeb are launching thousands of satellites for global internet coverage.
- AI and Automation in Space Operations – Autonomous spacecraft, AI-driven mission planning, and robotic assistance will enhance efficiency.
- Human Settlement on Mars and the Moon – NASA, SpaceX, and other organizations are developing permanent habitats beyond Earth.
- Space-Based Solar Power – Harvesting solar energy in space for transmission to Earth could revolutionize global energy markets.
- Regulatory and Policy Developments – Space governance, sustainability, and space traffic management will shape future operations.
Customer Insights
The space industry is expanding its customer base beyond governments and traditional aerospace firms. Key insights include:
- Growing Demand for Space Tourism – High-net-worth individuals and adventure seekers are early adopters of space travel experiences.
- Increased Commercial Investment – Corporations are leveraging space technology for telecommunications, remote sensing, and AI applications.
- Government and Defense Contracts – Nations are investing heavily in space capabilities for national security and scientific advancements.
- Sustainability Concerns – Consumers and regulators are demanding sustainable practices to reduce space debris and environmental impact.

Competitive Landscape
The space industry is highly competitive, with major players driving innovation and market expansion:
- Private Space Companies – SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Rocket Lab are leading in launch systems and commercial space ventures.
- Traditional Aerospace Firms – Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman continue to play key roles in government space contracts.
- Satellite Operators – Companies like SES, Viasat, and Starlink are reshaping global communications.
- Emerging Space Nations – Countries such as China, India, and the UAE are investing in independent space programs.
- Government Agencies – NASA, ESA, CNSA, and ISRO are setting policies and driving scientific missions.

Future Opportunities
- Lunar Economy and Base Development – The Moon will serve as a stepping stone for deep-space missions and a hub for scientific research.
- Commercial Space Stations – Private companies will develop and operate space habitats for research, manufacturing, and tourism.
- Space-Based Manufacturing – Zero-gravity environments will enable new materials and pharmaceutical production methods.
- Interplanetary Cargo and Logistics – Infrastructure for transporting goods and people between Earth, the Moon, and Mars will emerge.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems – Nuclear thermal and ion propulsion will enable faster and more efficient space travel.
- Space Law and Governance – Legal frameworks for ownership rights, conflict resolution, and resource sharing will be critical.

The space industry is poised for exponential growth by 2035, with significant advancements in technology, exploration, and commercial applications. While regulatory, financial, and sustainability challenges remain, strategic investments and collaborations between governments and private entities will unlock new opportunities for human space exploration and economic expansion beyond Earth.
















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Space Outlook 2035: Market