Ruminant Methane Reduction Market
The ruminant methane reduction market is estimated at USD XX million in 2024; it is projected to grow at a CAGR of XX% to reach USD XX million by 2029. Ruminants, such as cattle and sheep, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions through methane production, which not only harms the environment but also represents an inefficient energy loss for the animals themselves. As the agricultural industry seeks more sustainable production methods, researchers are actively investigating innovative approaches to reduce methane generation in the digestive systems of these animals.
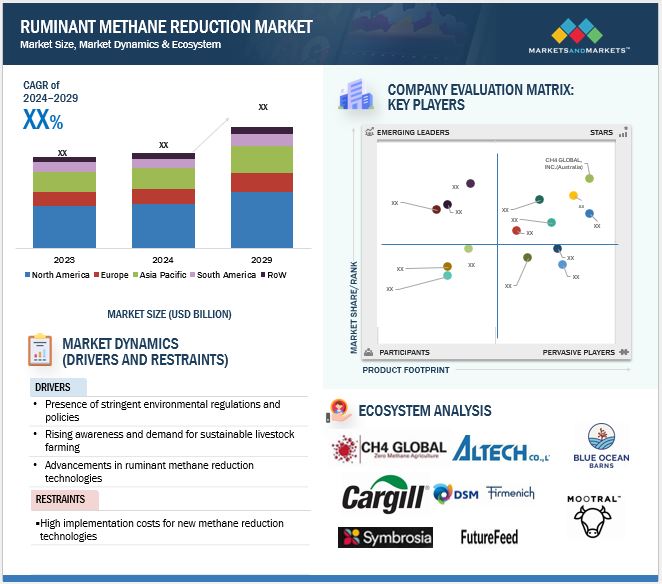

Market Dynamics
Drivers: Increased research and development (R&D) efforts are a significant factor driving the growth of the market
Collaborating with research institutions, agricultural organizations, and livestock producers provides potential to develop and commercialise effective methane reduction technology, increase animal production, and promote sustainable livestock farming practices. Taking advantage of this opportunity requires investment in research and development, regulatory clearances, field trials, and market adoption strategies for methane mitigation solutions and feed additives in the cattle business. In a landmark collaboration aimed at reducing methane emissions from cattle, agricultural solutions provider UPL and CH4 Global have forged a strategic partnership to distribute a groundbreaking seaweed-based feed supplement. Their Methane Tamer product, derived from Asparagopsis seaweed, promises to dramatically cut cattle methane emissions by up to 90%, targeting five key agricultural markets: India, Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay.
These countries, representing over 40% of the global cattle population, will serve as the primary testing ground for this innovative solution. The multi-year agreement leverages UPL's extensive distribution networks and feed formulation expertise, enabling widespread implementation of this environmentally transformative technology.
This partnership follows a broader trend of innovative approaches to agricultural sustainability, exemplified by recent investments like the Nissui Corporation's venture into Asparagopsis cultivation. By integrating natural, scientifically-developed solutions into existing agricultural practices, these initiatives represent a proactive approach to addressing climate change while maintaining livestock productivity.
Restraints: Biological Constraints
The ruminant digestive tract poses complex biological hurdles to methane reduction attempts. Ruminants, with their specialised four-compartment stomach, rely on a complex fermentation process assisted by methanogenic archaea. These microbes degrade complex carbohydrates, releasing methane as a natural metabolic byproduct. The symbiotic link between the animal and its gut bacteria is so important that eliminating methane production would drastically impair nutrition digestion.
Genetic variety hampers mitigating methods. Each ruminant species and individual animal has distinct genetic differences that influence microbiome makeup, digestive efficiency, and methane output. This heterogeneity makes designing a uniform methane reduction strategy extremely difficult, as measures that work for one species may be ineffective or hazardous to another.
Opportunities: Emerging technological innovations
Technological innovations are transforming agricultural methane reduction strategies, offering sophisticated solutions to mitigate livestock emissions through multifaceted approaches. The emerging technologies encompass a comprehensive array of interventions designed to address environmental challenges in animal agriculture.
Feed additives represent another pivotal technological intervention in methane reduction. Innovative supplements like Asparagopsis taxiformis, a seaweed-based additive, demonstrate remarkable potential by reducing methane emissions up to 80% when incorporated into cattle feed. These additives work by inhibiting methane-producing enzymes in the animal's digestive system, offering a direct and effective mechanism for emission reduction.
Challenges: Competition from substitutes and alternative feed additives
Although the warming effects of CO2 and methane are comparable, there are some differences between them. Compared to CO2, which remains in the atmosphere for centuries, methane only lasts for ten years but traps a lot more heat. Much more erratic are methane emissions, which come from coal mines, landfills, animals, and oil wells. The fact that most of the methane emissions from human activity come from sources that are widely distributed both within and between the five industries presents another difficulty. Between 40 and 50 percent of methane emissions worldwide are produced by agriculture, although these emissions originate from millions of farms of various sizes and farming methods worldwide.
Each methane reduction strategy involves critical trade-offs, balancing environmental benefits against potential unintended consequences. For instance, dry seeding in rice farming can reduce flooding-related emissions but potentially increase nitrous oxide output, another potent greenhouse gas. This highlights the intricate environmental calculations required in emission mitigation efforts.
The economic landscape of methane reduction is markedly uneven. In coal mining, abatement costs can be four to five times higher than leak detection methods in the oil and gas industry, primarily due to lower methane concentration levels. This significant cost disparity creates substantial challenges for individual companies considering comprehensive emission reduction strategies. The variations in abatement costs and technological feasibility create an uneven playing field that complicates widespread adoption of methane reduction approaches. Successful methane management will require continued technological innovation, nuanced economic incentives, and a holistic understanding of the multifaceted challenges inherent in emissions reduction efforts.
RUMINANT METHANE REDUCTION MARKET ECOSYSTEM

Prominent companies in this market include well-established, financially stable manufacturers of ruminant methane reduction technologies. These companies have been operating in the market for several years and possess a diversified product portfolio, state-of-the-art technologies, and strong global sales and marketing networks. Prominent companies in this market include Altech Co., Ltd. (Japan), Blue Ocean Matters (US), CH4 Global, Inc. (Australia), FutureFeed (Australia), Mootral (UK).
Based on product type, the feed additives/supplements sub-segment is projected to have a significant share in the market.
Feed additives dominate the ruminant methane reduction market due to their effectiveness in lowering methane emissions. These supplements contain compounds like nitrates, fats, tannins, and enzymes that modify ruminant digestive processes, specifically reducing methane production during enteric fermentation. The agricultural industry's increasing focus on sustainable practices has driven demand for these methane mitigation solutions, establishing feed additives as the leading product category in this market segment. Research in feed additives has uncovered innovative solutions that reduce methane emissions while maintaining animal health and productivity. Agolin SA's breakthrough additive, combining coriander seed oil, clove, and wild carrot extracts, demonstrates this progress. The supplement shifts rumen microbial populations, increases milk production, and cuts emissions by 10% per animal, attracting interest from livestock producers seeking sustainable solutions.
The cattle is the fastest growing segment in the ruminant methane reduction market is projected to have a significant share.
The fastest-growing segment among ruminant methane reduction by animal is cattle, propelled by several factors, including the significant contribution of cattle to global methane emissions, the increasing focus on sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation, and ongoing research and development efforts to develop effective methane reduction strategies specifically tailored for cattle. Additionally, the scale of cattle farming worldwide, and the environmental impact associated with methane emissions from cattle make this segment a key priority for innovative solutions and accelerated growth in methane reduction technologies and practices.
The increase in livestock population is a major factor propelling the market growth. As the global demand for meat and dairy products continues to rise, there has been a corresponding increase in the number of ruminant animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. Ruminant animals are known to produce methane as part of their digestive process, primarily through enteric fermentation in their rumen. This increased production contributes to climate change and highlights the urgency of implementing reduction measures. The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying reports that as per the 20th Livestock Census in India, there are approximately 303.76 million bovines (cattle, Mithun, buffalo, and yak), 9.06 million pigs, 148.88 million goats, 74.26 million sheep, and around 851.81 million poultry.
The North America region is anticipated to experience rapid growth between 2024 and 2029.
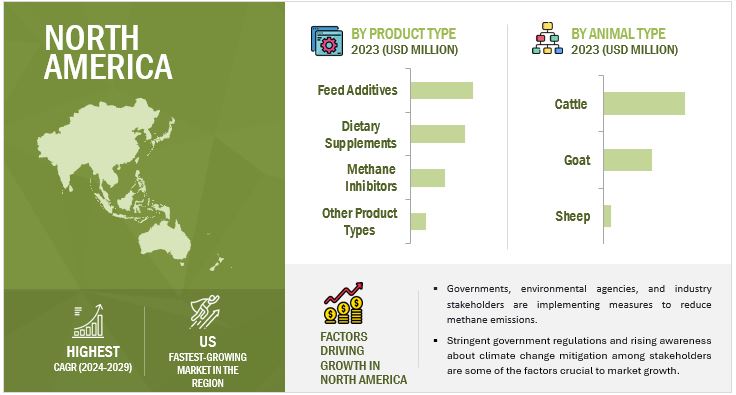
North America led the global ruminant methane reduction market with a significant market share in 2024. Substantial investments and financial incentives, such as the USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture's USD 10 million funding for emissions mitigation research in December 2023, are driving market expansion and sustainability in the region.
The US Ruminant Methane Reduction market is gaining momentum due to environmental concerns in agriculture. With methane being a significant greenhouse gas, there's increased focus on technologies that reduce emissions from livestock. This includes innovative feed additives, dietary modifications, and management strategies designed to improve digestion efficiency and minimize methane release, supporting the country's carbon reduction goals in agriculture.
Key Market Players
- Altech, Co., Ltd. (Japan)
- CH4 Global, Inc. (Australia)
- DSM (Netherlands)
- Blue Ocean Barns (US)
- Mootral (UK)
- Symbrosia (US)
- Zelp Ltd. (UK)
- Elanco Animal Health Inc. (Argentina)
- Rumin8 Limited (Australia)
- Cargill, Incorporated (US)
These market players are focusing on increasing their presence through agreements and collaborations. These companies have a strong presence in North America, Asia Pacific, South America and Europe. They also have manufacturing facilities along with strong distribution networks across these regions.
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, Rumin8, an Australian climate tech company, has received feed ingredient approval from Brazil’s Ministry of Agriculture for its methane-reducing supplement for livestock. This marks a significant step towards commercialization, especially in Brazil, which has the world’s largest cattle herd. Rumin8’s technology, using the compound Tribromomethane (TBM), has shown methane reductions of up to 86% and improved cattle weight gain in trials.
- In February 2024, dsm-firmenich and Donau Soja partnered to highlight the environmental impact of feed ingredients using Sustell, aiding businesses in measuring & improving sustainability in the animal protein value chain. Their collaboration aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from food production and enhance transparency in the feed & food industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the current size of the ruminant methane reduction market?
The ruminant methane reduction market is estimated at USD xx million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD xx million by 2029, at a CAGR of xx% during the same period.
Which are the key players in the market, and how intense is the competition?
Altech Co., Ltd. (Japan), Blue Ocean Matters (US), CH4 Global, Inc. (Australia). The market for ruminant methane reduction is expanding rapidly, with more mergers, acquisitions, and product launches. Companies in this sector are also heavily investing in research and development.
Which region is projected to account for the largest share of the ruminant methane reduction market?
The North America market is expected to dominate during the forecast period. The region currently stands as a formidable force in the ruminant methane reduction market, boasting dominance fueled by a convergence of factors, including robust research and development initiatives and the presence of major key players with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
What kind of information is provided in the company profile section?
The provided company profiles deliver crucial details, including a thorough business summary that covers different segments, financial results, geographic presence, revenue distribution, and business revenue breakdown. They also offer insights into product lines, key achievements, and expert analyst opinions to better illustrate the company's potential.
What are the factors driving the ruminant methane reduction market?
Stringent government regulations and rising awareness about climate change mitigation among stakeholders are some of the factors crucial to market growth.
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst
















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Ruminant Methane Reduction Market