PFAS Waste Management Market By Substance Type (PFOS, PFOA, PFBA, PFDA), Waste Type, Treatment Method (Incineration, Landfilling, Recycling, Solidification), PFA Content, Service Type, Source Type (Industrial, Military, Construction, Municipal), And Region - Global Forecast to 2029
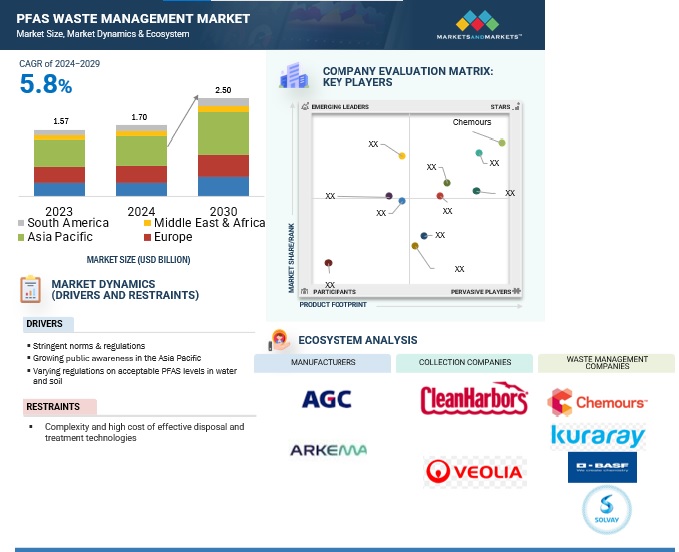
The global PFAS waste management market is estimated to reach USD 2.50 billion by year 2029 from USD 1.70 billion in year 2024, at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. The market is propelled by factors such as the rise in regulatory actions and public awareness. Governments all over the world especially those in the United States and Europe are putting policies in place to address PFAS pollution. For instance, some of the restrictions regarding the use of certain PFAS have been proposed by the European Union under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorizations, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) while the (US) Environmental Protection Agency has put forward concentrations of PFAS in drinking water. Moreover, legal actions and legal exposures concerning contamination cases have forced industries to look for efficient waste management services. Growth is further stimulated by developments in remediation technologies such as incineration, advanced oxidation, and other methods including electrochemical treatment and activated carbon filtration. R&D investments in eco-friendly PFAS destruction approaches, along with the financial support of big-scale remediation projects, support market growth. The increased need for better and safer ways of controlling the generation and disposal of waste also offers room for entrepreneurs dealing with technologies in waste-to-energy conversion, and environmental rehabilitation.
ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES IN THE PFAS WASTE MANAGEMENT MARKET
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report

PFAS Waste Management Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing regulatory pressure from governments and environmental agencies worldwide
One of the major factors which will help mainly drive the PFAS waste management market in the coming years is the rising global pressure from governments and environmental organizations. PFAS also known as ‘‘forever chemicals’’ have raised an alarm concerning their impacts on the environment and human health, and therefore regulatory bodies have enhanced stringent measures on the management of PFAS-contaminated sites. For instance, The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has largely limited the allowed concentrations of PFAS in drinking water under the Safe Drinking Water Act and the European Union restricts PFAS-specific usage gradually under the REACH regulation. Not only are these measures forcing industries to adopt best practices in waste management but also create emphasis on large quantum cleanup of contaminated sites. The costs of nonconformity make the need for proper PFAS waste management even more compelling. The authorities found it important because industries, particularly the manufacturing, firefighting, and chemical processing industries, continue to face legal risks resulting from PFAS contamination. Moreover, public awareness and legal battles by the affected public have put on the spotlight the issue of compliance with the regulations. These three factors all work in harmony: legislative and legal requirements as well as the public’s increasing awareness have motivated the development of technologies to remove PFAS and make regulation a central factor for growth in the waste management market.
Restraints: High cost and technical complexity associated with effective PFAS remediation and disposal
A major controller of the PFAS waste management industry is the high cost and enhanced feasibility of the PFAS treatment and disposal techniques. Unlike other conventional pollutants, PFAS is very stable and cannot readily be degraded due to its unbreakable carbon-fluorine bonds meaning that PFAS removal and destruction requires sophisticated and high energy-demanding technologies such as incineration, advanced oxidation processes, or plasma destruction. These methods also entail expensive capital investment, sophisticated apparatuses, and expert staff, features that are hard to justify in the case of industries or municipalities with tight budgets.
Moreover, the absence of generally agreed-upon procedures and doubt regarding the complete elimination of PFAS compounds also persists as a challenge for applications. For example, people are questioning the effectiveness of incineration and inadequate combustion has been reported to have an adverse impact. Some regions lack proper regulatory mechanisms that complement those in this paper, making the disposal of PFAS waste even more uncoordinated globally. In addition, all these factors acting in unison pose a major challenge to the implementation of PFAS treatment solutions and keep back stakeholders from fully embracing effective advanced waste management systems. These obstacles will have to be addressed through collective efforts in research grants, revising and integrating the requisite standards for regulation as well as employing low-cost technologies amenable to widespread application in all sectors.
Opportunity: Development and commercialization of innovative, cost-effective treatment technologies
A primary analysis of the current state and future of the PFAS waste management market reveals a major opportunity: the identification of new technologies for the effective and affordable treatment of PFAS-contaminated wastes. New technologies like electrochemical oxidation, third-generation adsorbent materials, and bioremediation appear to fix the technical and economic issues encountered in conventional PFAS remediation. These technologies are intended to search for better solutions to degradable PFAS into harmless components without using a lot of energy as the other methods offered such as incineration and the advanced oxidation processes. Industry analysts agree that strict implementation of environmental measures presents a good market that companies embracing related technologies can benefit from. For example, venture organizations tech startups, and research institutions are working towards advancing end-user technologies such as carbon-based adsorbents and catalytic processes to enhance the methods of PFAS removal. Moreover, the government established programs and funding for R&D in PFAS treatment which is supported in North American and European countries. Since industries and municipalities look for ways and means to address the PFAS waste issue with inexpensive and regulatory solutions in mind, the above-mentioned technologies will witness greater usage. This demand has the potential to build an exceedingly firm market for PFAS waste management across the globe, specifically for the enterprises that are engaged in the provision of innovation and scalability-based solutions to this issue.
Challenges: Lack of global regulatory uniformity
One of the major issues within the PFAS waste management market is the absence of standardized rules for disposing of material all over the world. The regulations that were set to tackle PFAS presence have been imposed in most countries, but variations in the implemented rules’ rigor and effectiveness persist. For example, while the United States EPA had established range standards for PFAS in drinking water, several European nations are on the path to blanket bans and strict allowable concentrations under the REACH regime. However, many developing countries still have no standard guidelines for the management of PFAS hence the irregularity of practices in the World today. What is more, regulatory fragmentation becomes a problem for industries and municipalities, as a company operating in different regions faces different rules and standards. Second, there has been no clear protocol on how to use the available technologies in handling PFAS including incineration and adsorption hence complicating waste management efforts. Such discrepancies hamper cross-national cooperation and the exchange of strategies concerning the management of PFAS pollution. To overcome this challenge, there is a need for international cooperation to align the policies to attain standards recognized internationally for the detection, removal, and elimination of PFAS. Without such efforts, PFAS waste management therefore remains constrained and will not advance the state-of-art in eliminating the far-reaching environmental and health effects of these chemicals.
PFAS Waste Management Market Ecosystem
The PFAS waste management market ecosystem consists of a complex network of stakeholders, technologies, and regulatory frameworks that work together to address the environmental and health challenges posed by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). These companies have been operating in the PFAS waste management market for several years and comprises of diversified product portfolios and strong global sales and marketing networks.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, and MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Industrial manufacturing is the largest source of PFAS waste management market during the forecast period
Industrial manufacturing is the biggest contributor of PFAS wastes because PFAS is used in so many industries in so many capacities. Applications of PFAS are present in multiple industries, especially textiles, electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries since it has properties like thermal stability, resistance to oil, and water. Some of the products where PFAS is used during their production include non-stick coatings, waterproof materials, and fire-resistant products and these give out PFAS through emissions, wastewater, or solid wastes.
Manufacturing industries emit PFAS compounds more frequently as these are created, used or transformed to form other products at chemical industries. For example, factories producing firefighting foams or industrial lubricants produce large amounts of PFAS waste. Further, the outcomes of many such processes pollute water supplies and soils in the region and become long-term problems.
The PFAS waste generation from industries indicates the importance of regulatory control and the development of wasteful technologies. Techniques like on-site filtration, waste collection devices, and enclosure linked with aggressive handling and disposal strategies including incineration or plasma conversion are on the rise to reduce the effects. Nevertheless, cleaning up the contamination left behind by decades of industrial PFAS usage has proven difficult in many countries to date.
Incineration held the largest market share in 2023, accounting for over 40% of the global market share due to its effectiveness in destroying PFAS compounds
Incineration led the PFAS waste management in year 2023. The reason behind this is the method itself has effectively managed to resolve the challenge in breaking the powerful C-F bond of PFAS compounds, hence being noreactive and less harmful to the environment. Disposal by extreme heat, namely above 1,000°C, makes it possible to eliminate PFAS particles, which hardly decompose under normal combustion conditions and other wastewater treatment processes.
Incineration is preferred by industries and governments because it can accept a very high load of contaminated materials such as industrial sludge, contaminated soil, and municipal waste. It is most commonly used in the elimination of PFAS-containing firefighting foams and industrial wastes — leading sources of PFAS contamination. Sophisticated purification technologies for the gaseous output of air pollutants ensure that even if solid wastes are incinerated, hazardous byproducts of the process are reduced to acceptable limits.
Nevertheless, the efficiency of this method provokes criticism linked to such factors as the incompleteness of combustion and generation of secondary emissions of hydrogen fluoride and ultra-short-chain PFAS compounds. These challenges show that constant research, monitoring, and development of techniques for effective incineration are still necessary to retain this industry at the top.
Asia Pacific is estimated to be the fastest-growing region in the PFAS waste management market
The Asia Pacific region is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period due to tremendous industrialization, increasing awareness of the environment, and government initiatives. From the PFAS waste management market viewpoint, the Asia Pacific is expected to be the most rapidly increasing market owing to increasing industrial activities, population density, and increasing consciousness of people regarding the pollution level and impacts caused due to Aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs). Recent developing countries like China, India, and Japan are contaminated largely by industrial growth which includes textile, electronics, and automobile industries that use a lot of PFAS. Several countries' regional governments have put in place measures to reduce the emission of PFAS chemicals to the environment. For instance, China has set up its guidelines and policies for emissions and contamination, and Japan has been more advanced in regulating PFAS at industrial levels. Also, the constant technological development of innovations, corresponding to waste management, through investments by governments and private corporations, increases the market growth rate. This has been boosted by the large population base of the region and the growing need for clean water and environmentally friendly approaches to waste disposal. Furthermore, an increase in public awareness about PFAS water pollution and global organizations’ joint efforts to reduce it increases the market potential. As technologies of remediation proliferate and such legislation continues to gain traction, Asia Pacific is expected to steer the PFAS waste management market’s growth worldwide.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
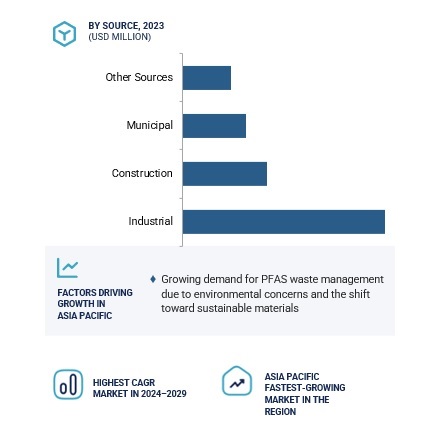
Key Market Players
Key players in this market include Chemours (US), Asahi Glass (India), Kuraray (Japan), Arkema (France), BASF (Germany), Shandong Chengxin Chemical (China), DIC Corporation (Japan), 3M (US), Daikin Industries (Japan), Huntsman Corporation (US), Solvay (Belgium), AGC Chemicals (US), Haike Chemicals (China), Clean Harbors, Inc. (US), Veolia (France), TerraTherm (US), Clean Management Environment Group, Inc. (US), Evoqua Water Technologies LLC (US), Chemviron (Belgium), Republic Services, Inc. (US), Newterra (US), Indaver (Belgium), WSP (Canada), OPEC Systems Pty Ltd. (Australia), and Wanless Waste Management (Australia).
Recent Developments in PFAS Waste Management Market
- During the month of February 2023, Daikin Industries continued to deal with PFAS emissions as all American and European manufacturing facilities of the company reduced process water discharges to 99% of processing aids. Efforts in this regard have also been considered part of accomplishing one of their visions; reduction of PFAS effect on the environment. Daikin is also currently seeking new technology and working methods to guarantee even safer production and handling of PFAS-related materials. These campaigns emphasized Daikin’s commitment to embrace changes that would ensure PFAS waste management meets the growing environmental concerns as well as compliance with global legal requirements.
- In April 2023, Solvay has been very active in addressing the PFAS waste problem on the technological side as well as through legal claims. To the claims pertaining to PFAS regulations, the company set an agreement with the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP). This settlement was to comprise USD 75 million as natural resource damages and USD 100 million to fund various remediation projects. Under the settlement, Solvay also agreed to step up its environmental obligations and expend USD 214 million for continuing PFAS-related remedial work. Moreover, Solvay has been gradually phasing out the use of fluorosurfactants in manufacturing it aims to produce close to 100% of its fluoropolymers without these substances by 2026.
- In August 2024, Clean Harbors introduced “Total PFAS Solution,” an integrated offering that addresses PFAS (per and polyfluorinated alkyl substances) content. It is a complete service, which is an industry first with analysis, remediation, and responsible disposal of PFAS waste. Its measures employ thermal degradation, whose proficiency in eradicating PFAS is well illustrated by their burning capacities, which are all over 99.9999 %, thus meeting regulatory measures. Clean Harbors is also proactively marketing it for this offering in expectation of enhanced legislation on account of PFAS categorization as emerging substances of environmental concern besides the likelihood of other authorities such as EPA and the Department of Defense upping their regulatory pursuits on the back of such chemicals. It connects Clean Harbors to the growing need for managing the so-called “forever chemicals” and expands its position in the sector of PFAS waste management.
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What primary factor is propelling the growth of the PFAS waste management market?
The primary factor propelling the growth of the PFAS waste management market is the increasing regulatory scrutiny and environmental concerns associated with PFAS contamination.
How is the PFAS waste management market segmented?
In this report, the PFAS waste management market is segmented based on substance type, waste type, source, treatment method, PFA content, service type, and region.
What are the major challenges in the PFAS waste management market?
The complexity and high cost of effective disposal and treatment technologies are the major challenges of PFAS waste management.
What are the major opportunities in the PFAS waste management market?
Growing demand for advanced and efficient treatment technologies, driven by stricter regulations and rising public awareness about the environmental and health risks posed by PFAS, are opportunities for PFAS waste management companies over the next five years.
Which region has the largest demand?
The Asia Pacific region stands out with the highest demand for PFAS waste management.
Who are the major manufacturers of PFAS waste management?
Major players in the PFAS waste management market are Chemours (US), Asahi Glass (India), Kuraray (Japan), Arkema (France), and BASF (Germany).

PFAS Waste Management Market















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in PFAS Waste Management Market