Electric Mid- and Large (9-14m) Bus Market Technology Landscape, Trends and Market Analysis by Propulsion (BEV, FCEV, HEV/PHEV), Configuration (Light & Heavy Duty), Application (City/Transit Bus, Coach, Midi & School Bus) and Region - Global Forecast 2030
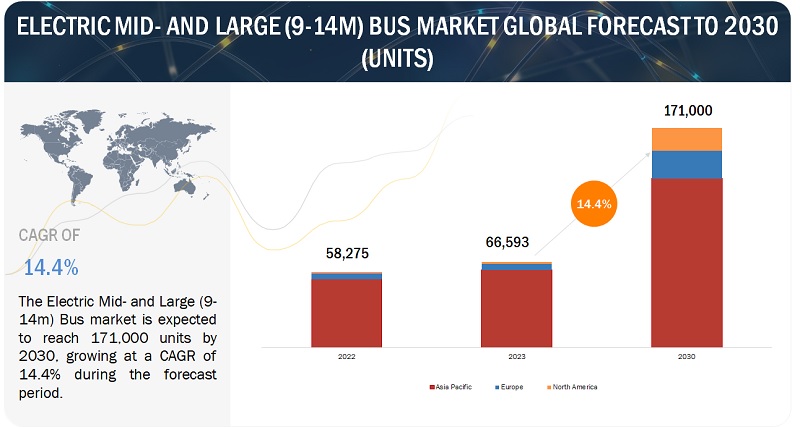
[121 Pages Report] The electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market is expected to grow from 66,593 units in 2023 to 171,000 units by 2030, with a CAGR of 14.4% from 2023 to 2030. The market is driven by factors such as demand for zero-emission vehicles, growing environmental concerns, and government initiatives promoting sustainable transportation drive the electric mid- & large bus market.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Dynamics:
DRIVER: Growing need for green mobility solutions
The widespread adoption of electric mid- & large buses is poised to gain momentum globally, propelled by factors such as stringent emission regulations, declining battery prices, the establishment of low-emission zones, government purchase subsidies, and tax exemptions. This surge in the embrace of electric transit buses has facilitated the development of a global supply chain for alternative powertrain buses. The escalating imperative to curb emissions, particularly in densely populated urban centers, will drive the demand for electric mid- & large buses in intra-city passenger transportation. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), a substantial increase in the global production of batteries for electric mid- & large buses, featuring a 100 kWh capacity for Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), from 25,000 to 100,000 units annually, has the potential to significantly slash battery pack production costs per kilowatt-hour by 13%, nearly one-third lower than the existing price of USD 300/kWh. It is noteworthy that the cost of batteries is directly linked to their capacity, and while initial prices for high-capacity batteries were elevated, ongoing reductions have made them more economically viable for end users. Ongoing research is also focused on expanding battery pack sizes to support the diverse range requirements of electric mid- & large buses while concurrently reducing overall costs. With declining lithium prices, the adoption of electric mid- & large buses is expected to rise in future.
Restraint: EV Batteries related safety issues
While EV batteries used in electric mid- & large buses undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety, the US National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) reports that a notable portion of EV fires in the US between 2013 and 2017 were attributed to battery power systems. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, heavy rain, and overcharging were identified as primary contributors to EV battery fires. To address safety issues, manufacturing companies globally, including those in the US, China, Japan, and the European Union (EU), are mandated to prioritize continuous monitoring of battery safety, health, and performance. Specific electric mid- & large bus standards focus on limiting chemical spillage, securing batteries during crashes, and isolating the chassis to prevent electric shock. Additionally, ensuring optimal working temperature and protection necessitates advanced battery management systems, but their development demands a substantial investment of time and resources from manufacturers. The increased development costs subsequently impact the overall initial cost of electric vehicles, posing a financial burden on buyers. In the electric mid- & large bus context, the size of the battery pack, influenced by driving range requirements, directly affects the cost and complicates the vehicle's body and chassis design. Given that these batteries may require replacement once or twice during the bus's operational life, contingent on factors like annual distance traveled, operating temperature, and charging rates, the associated high initial and maintenance costs emerge as significant constraints for market growth
Opportunity: Innovation in Payment Models
Electric mid- & large bus will see a significant shift in the purchasing behaviors of operators and cities. This will see shifts away from CAPEX to OPEX based purchasing, including the utilization of new business models such as “bus-as-a-service”, “battery-as-a-service” and “depot-as-a-service” due to the increased CAPEX cost of eBus’s and the requirements for long term support of batteries and infrastructure. For public transport operators, NXP’s Mifare introduced smartcards and NFC ticketing solutions. In most cities, the original transit cards are no longer necessary.
Challenge: Developing charging infrastructure requires huge capital investment
Electric mid- & large buses face a trade-off between longer charging durations and a lower driving range per charge, with battery performance and lifespan crucially influencing both their effectiveness and costs. Lithium-ion batteries are progressively displacing lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, and nickel-metal hydride batteries in Electric mid- & large buses due to their extended lifespan. However, lithium-ion batteries exhibit limitations in capacity for powering heavy commercial vehicles like electric mid- & large buses, particularly in cold climates where charging-discharging efficiency decreases, impacting power delivery. According to Molecular Diversity Preservation International (MDPI), current electric mid- & large buses grapple with insufficient battery capacity, affecting their cooling capabilities. Presently available charging infrastructure also contributes to longer charging times, with the average duration to charge an electric mid- & large bus from 0% to 100% at a 7-kW charging point exceeding 4 hours. Additionally, industry experts highlight the need for an expanded network of charging stations, particularly in urban areas of Europe, North America, and other developed regions. Disparities in charging infrastructure are noted, with fewer charging stations in Eastern Europe compared to Northern Europe.
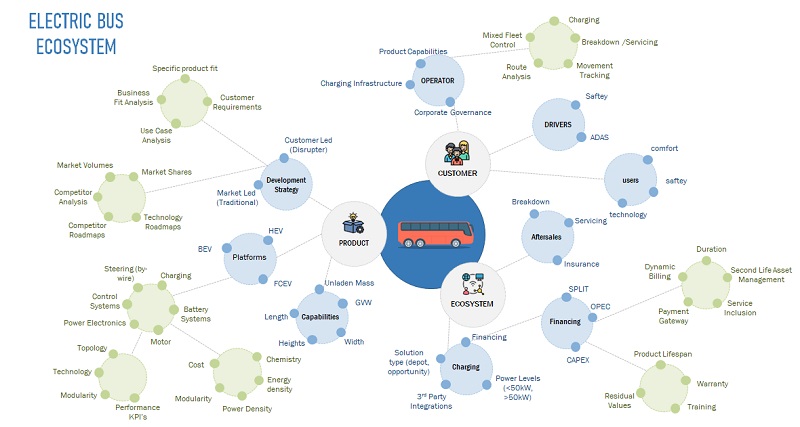
Market Ecosystem
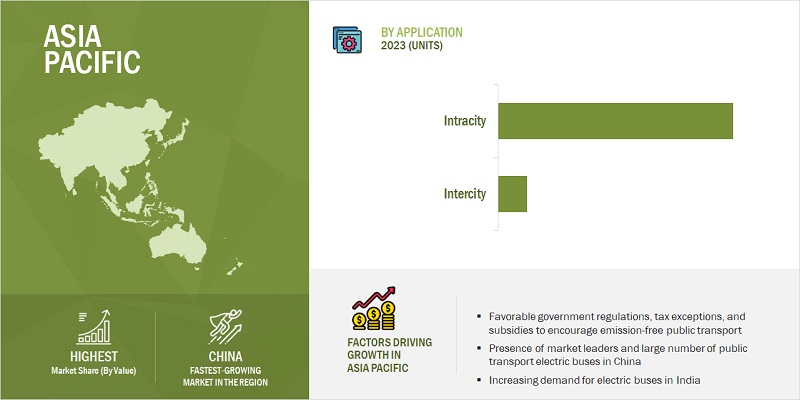
City/transit bus to dominate the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market, by application
Electric mid- & large buses for city/transit applications are mostly preferred across Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America. The growth is mainly attributed for these buses as it is well-suited for use in urban areas and can carry many passengers as this segment's relatively larger seating capacity and easy to manoeuvre through narrow city streets and navigating around city traffic. Moreover, the offered battery range in these buses are adequate for most urban transit routes and can undergo relatively quick charging, rendering them practical for daily operations by public transport bodies. However, electric mid- & large buses are also manufactured in alternative sizes, such as mini-buses and double-deckers, catering to specific purposes like airport shuttles or tourist routes. The growth in adopting electric transit buses has enabled global sourcing and supply chain for alternate powertrain buses. The increasing need for reducing emissions, especially in highly populated cities, will amplify the demand of electric mid- & large buses for city/transit application.
LFP is expected to be the fastest-growing battery type for electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus.
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are expected to hold the largest share during the forecast period. LFP batteries offer several advantages as it is lightweight, low-priced, and higher thermal stability with enhanced discharge and charge efficiency than NMC batteries. It has a longer life span, have minimal maintenance, and offer optimized safety. Due to these advantages, LFP batteries are extensively used in high-performance electric mid- & large buses, delivering a high current rate, ensuring high voltage bearing capability and possessing a long cycle life. Moreover, LFP batteries are also preferred choice for long-haul buses, as they can support heavy battery packs constructed with low-density cells, meeting the necessary range requirements.
As the prices of LFP batteries are lower than NMC and NCA batteries, Asia Pacific lead the adoption of LFP batteries in electric buese. For instance in September 2022, BYD Company Ltd. has developed blade battery technology which uses LFP chemistry, promise to offer 40-50% more energy density capacity. Some electric mid- & large buses which are deployed with this chemistryare Yutong E12, BYD K9, Zhongtong Bus LCK6125EVG, King Long XMQ6127EVG, Ashok Leyland Circuit, and Olectra BYD eBuzz K9 among others. With advancements in battery technology and a continuous drop in battery prices, the further boost in the demand of LFP battreies are expected to rise in electric mid- & large buses.
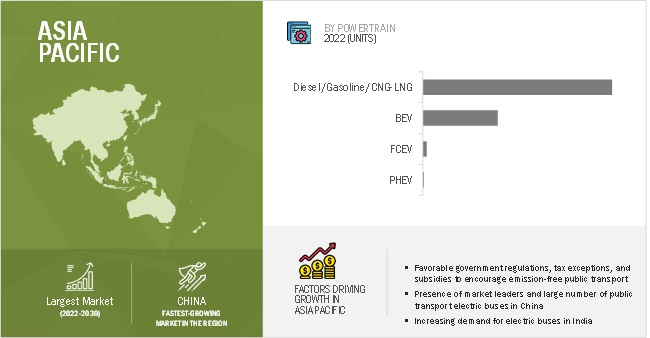
The Asia Pacific region is the largest electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market during the forecast period
Asia Pacific is the largest market for electric mid- & large buses globally throughout the review period. The key reason of the higher regional demand is the increasing need to reduce urban pollution and dependency on fossil fuels in this region, along with growing government initiatives toward clean public transportation. China is the largest market globally, accounting for over 95% of the market share in 2022. Chinese companies such as BYD, Yutong, Ankai, and Zhongtong dominate the Chinese as well as global electric mid- & large buses markets. Chinese players have developed and offered electric mid- & large buses at lower prices due to the availability of parts and components at lower rates. Most Chinese bus manufacturers have fully electric and hybrid buses in their portfolio and focused on providing and redefining mass transportation and have won several orders for e-buses. Further, the policies of Chinese government favor electric mid- & large buses over ICE ones such as priority access to bus lanes, exemptions from certain traffic restrictions or congestion charges, and preferential parking policies. Under New Energy Vehicle Subsidy Program, it offers subsidies depending on the size and range, for the purchase of new energy vehicles, including electric mid- & large buses. For example, a 12-meter electric bus with a range of 200 kilometers can receive a subsidy of ¥500,000 (USD 75,000). Thus, China will continue to play a key role in the future of both the ebus and overall bus market and with a >40% market share maintained for both through 2030.
Many of the leading players in the electric mid- & large buses market, including BYD (China), Yutong (China), King Long (China), Zhongtong (China), Tata Motors (India), Ashok Leyland (India), JBM Auto Limited (India) and many others are from Asia Pacific. Furthermore, the rapid expansion of the electric mid- & large buses fleet in several countries in this region is also a key driving factor for the region to dominate the electric mid- & large bus market. The reduction in the batteries and EVs cost, and the development of charging infrastructures, also provide a great opportunity for the growth of the electric mid- & large bus market. Many countries in the Asia Pacific region, including China, South Korea, India, and Japanese markets, have favorable government policies and mandates that promote the reduction of emissions and usage of green technology in public transportation.
China, being the largest market for automobiles in the world and with the intention of being the number one electric vehicle market, has been in the forefront in this market since 2009. In August 2022, the government of Hainan province proposed a complete ban on the sale of combustion cars by 2030 in its implementation plan for peaking carbon emissions. The amount of the subsidy depends on the size and fuel efficiency of the vehicle. For example, a 12-meter electric bus with a fuel efficiency of 1.2 kilometers per kilowatt-hour can receive a subsidy of ¥300,000 (USD 45,000).
Most of the Chinese electric mid- & large bus players such as BYD are equipped for to manufacture a greater number of components in-house, mainly to reduce the expenses and ensure the quality. The Chinese OEMs including King long and Yutong are turning to export market to keep their manufacturing facilities running at high utilization rates.
Key Market Players
The key players in the electric mid- & large bus market BYD (China), Yutong (China), CAF (Solaris) (Spain), VDL Groep (Netherlands), and AB Volvo (Sweden). The key strategies adopted by major companies to sustain their position in the market are expansions, contracts and agreements, and partnerships.
To analyze and forecast the trends and orientation for the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market in the global industry.
Scope of the Report
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Market size available for years |
2019–2030 |
|
Base year considered |
2022 |
|
Forecast period |
2023-2030 |
|
Forecast units |
Volume (Units) |
|
Segments Covered |
Application, Propulsion, and Region |
|
Geographies covered |
Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America |
|
Companies Covered |
BYD (China), Yutong (China), CAF (Solaris) (Spain), VDL Groep (Netherlands), and AB Volvo (Sweden) |
This research report categorizes the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market based on Application, Propulsion Type, and Region.
Based on Application:
- City/Transit Bus
- Coaches
- Midi Bus
- School Bus
Based on Propulsion:
- BEV
- FCEV
- HEV/PHEV
- Diesel/Gasoline/CNG-LNG
Based on the Region:
- Asia Pacific
- North America
- Europe
Recent Developments
- In January 2022, the Valley Transportation Authority (VTA) in Santa Clara City, US, will install an innovative clean energy microgrid and EV fleet charging system with Proterra and Scale Microgrid Solutions. This project will showcase how clean energy paired with fleet-scale EV charging can enable the adoption of fully electric vehicle fleets. Expected to come online in late 2023, it will help VTA further reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- In January 2023, Daimler received an order to supply 45 buses to VLP Transport for intercity transport.
- In September 2022, the Urbino 18 model is equipped with a modern hydrogen fuel cell, which aids long-distance commuting as it can cover 350 km in a single refill with a passenger capacity of 138 seats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the current size of the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market by volume?
The current size of the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market is estimated at 58,273 thousand units in 2022.
Who are the winners in the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market?
The electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market is dominated by BYD (China), Yutong (China), CAF (Solaris) (Spain), VDL Groep (Netherlands), and AB Volvo (Sweden), and among others. These companies manufacture trains and develop new technologies. These companies have set up R&D facilities and offer best-in-class products to their customers.
What are the recent innovations in the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market considering the level of autonomy?
Many OEMs are actively developing level 4/5 autonomous electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus, which can intelligently control acceleration, steering, driving environment monitoring, and dynamic driving tasks. For instance, in 2021, Iveco Bus (Netherlands) and driverless technology provider EasyMile (France) partnered and completed testing a fully driverless standard bus prototype capable of operating under real conditions.
How does bus electrification impact the other players in the ecosystem?
Because of the increasing electrification of buses, other players such as tier I and tier II suppliers, including components suppliers, engine manufacturers, and others, have started to develop components that are demanded in the electric mid- & large bus market.
What are different countries covered in Asia Pacific region for electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market?
The countries covered in report for electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market are China, Japan, India, South Korea. .
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst

The study involved four major activities in estimating the current size of the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, peer, and child markets. The next step was to validate these findings and assumptions and size them with industry experts across value chains through primary research. The bottom-up and top-down approaches were employed to estimate the market size. After that, market breakdown and data triangulation processes were used to estimate the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
In the secondary research process, various secondary sources were used to identify and collect information for this study. The secondary sources include annual reports, press releases, and investor presentations of companies; whitepapers, certified publications; articles from recognized authors, directories, and databases; and articles from recognized associations and government publishing sources. Secondary research has been used to obtain key information about the country-wise electric mid- & large bus sales, the overall pool of key players, market classification and segmentation according to industry trends to the bottom-most level, regional markets, and key developments from the market- and technology-oriented perspectives.
Primary Research
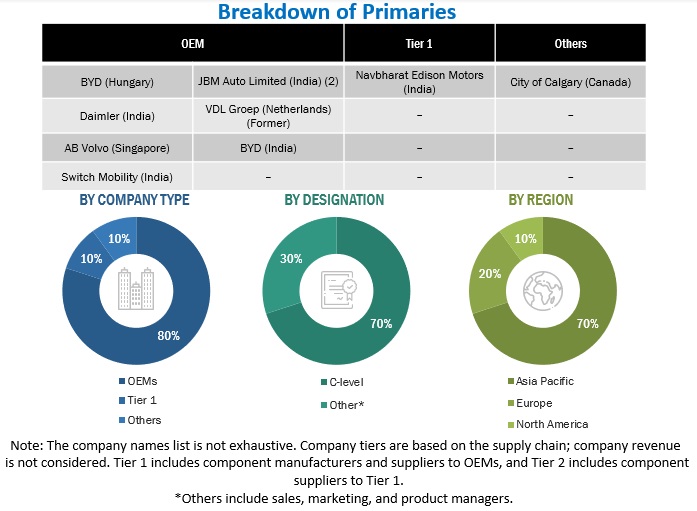
After understanding this market scenario through secondary research, extensive primary research has been conducted. Several primary interviews have been conducted with market experts from the demand- and supply-side OEMs (in terms of component supply, country-level government associations, and trade associations) and component manufacturers across three major regions: Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America. Approximately 80% and 20% of primary interviews were conducted with the OEM and Tier I/Tier II players, respectively. Primary data was collected through questionnaires, emails, LinkedIn, and telephone interviews. In the canvassing of primaries, we have strived to cover various departments within organizations, such as sales, operations, and administration, to provide a holistic viewpoint in our report.
After interacting with industry experts, we conducted brief sessions with highly experienced independent consultants to reinforce the findings from our primaries. This and the in-house subject matter experts’ opinions have led us to the findings described in the remainder of this report. Following is the breakdown of primary respondents.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
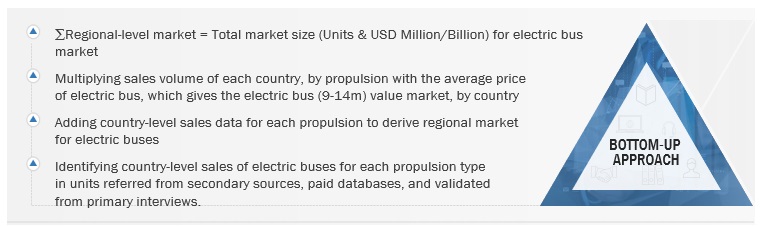
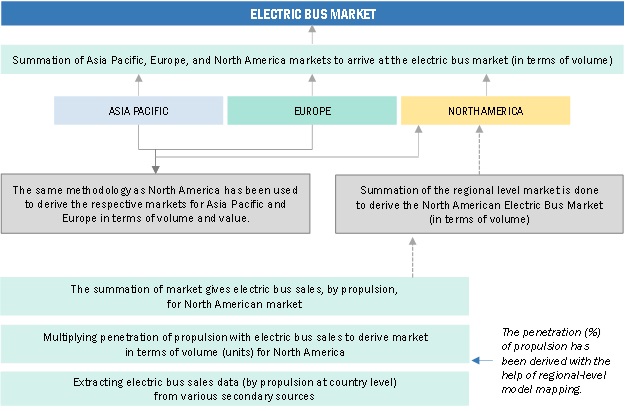
Bottom-Up Approach: Electric Mid- And Large (9-14m) Bus Market
The bottom-up approach was used to estimate and validate the size of the electric mid- & large bus market. The size of the electric mid- & large bus market, by propulsion, in terms of volume and value, was derived by collecting country-level sales of electric mid- & large buses by length (in units). This gives the historic and base year volumes for electric mid- & large buses. Further, the summation of all countries led to the regional-level market in volume.
Bottom-Up Approach: By Propulsion
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Bottom-Up Approach: By Region
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall size of the vehicles complying with the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus Market through the methodology mentioned above, the market was split into several segments and subsegments. Data triangulation is a research technique used to increase the validity and reliability of findings by cross-validating data from multiple sources or methods. This technique involves the use of multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, and secondary data, to confirm and corroborate the findings obtained from each source. The extrapolated market data was triangulated by studying various macro indicators and regional trends from both the supply and demand sides.
Market Definition
Electric mid- & large bus operate solely on batteries, whereas hybrid buses employ a blend of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) and battery power. These buses are utilized for the mass transit of passengers, with charging options including off-board top-down pantograph, on-board bottom-up pantograph, and connector methods. As outlined by Proterra, an electric bus relies on one or more electric motors fueled by a battery or a hydrogen fuel cell system. In line with BYD from China, an electric bus is defined as a bus propelled by an electric motor and a battery pack, which receives its charge by connecting to an electric power source.
List of Key Stakeholders
- Associations, Forums, and Alliances Related to Electric Vehicles
- Automotive Investors
- Automotive Software Manufacturers and Providers
- Companies Operating in Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystem
- Electric Mid- & Large Bus Manufacturers
- Electric Pick-up Truck Manufacturers
- Electric Truck Manufacturers
- Electric Van Manufacturers
- EV Charging Equipment Manufacturers
- EV Charging Infrastructure Service Providers
- EV Component Manufacturers
- EV Component Suppliers
- EV Distributors and Retailers
- Government Agencies and Policy Makers
- Battery Distributors
- Battery Manufacturers
- Charging Infrastructure Providers
- Charging Service Providers
- Companies Operating in Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystem
- Distributors and Retailers
- Original Equipment Manufacturers
- Raw Material Suppliers for Automotive Software or Components
- Transport Authorities
- Technology Providers
- Vehicle Electronics Manufacturers
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, and forecast the size of the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market in terms of volume (units) based on
- Propulsion (Diesel/Gasoline, BEV, HEV/PHEV, and FCEV)
- Application (City/Transit Bus Coaches, Midi Buses, and School Bus)
- Region (Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America)
- To understand the overall electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus ecosystem, value chain analysis, TCO analysis, technology analysis, and major electric mid- & large bus models in the global market
- To understand the dynamics of competitors in the electric mid- and large (9-14m) bus market and their product portfolio strength and business strategies
- To analyze opportunities for stakeholders and the competitive landscape for market leaders
- To strategically profile key players and comprehensively analyze their market share and core competencies.
- To track and analyze competitive developments, such as new product launches, deals, and other developments by key players.
-
Available Customizations
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations in accordance with company-specific needs.
- Deep-dive country-level analysis of electric mid- and large (9-14m) buses, by Application (For countries covered in the study)
- Deep-dive country-level analysis of electric mid- and large (9-14m) buses, by Battery type (For countries covered in the study)















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Electric Mid- and Large (9-14m) Bus Market