Cyber Warfare Market by Solution (Threat Intelligence, Data Protection, Security and Vulnerability Management, Identity and Access Management, Managed security solution, Resilience Solution) End User (Land, Naval, Airborne, Space), Application (Cyber Defense, Cyber Resilience), & Region - Global Forecast To 2029
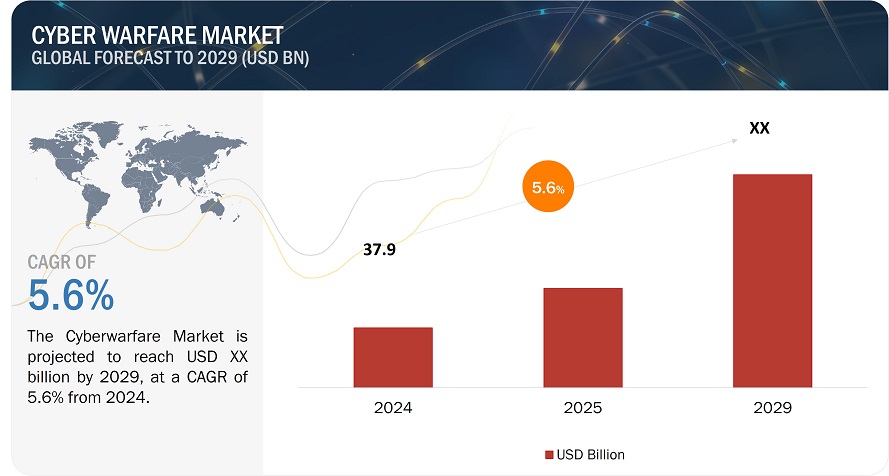
Cyber Warfare Market Overview
The global market of cyber warfare is presently under rapid growth, being facilitated by continuously advanced nature of the threat of cyber-attacks along with dependence of global defense on its infrastructure. The entire security scenario of these forces involves substantial spending on cutting-edge protection products for data, thereby augmenting its size massively in the global market of cybersecurity. Emerging technologies such as AI, ML, and quantum computing are part of cyber-defense strategies today. It increases their ability to detect threats as well as respond. Many key players are establishing strategic partnerships and investing greater R&D efforts in such areas with the growing demand of the nature of Cyber Warfare. This market will help shape future modern warfare for sure because of strong growth in its regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
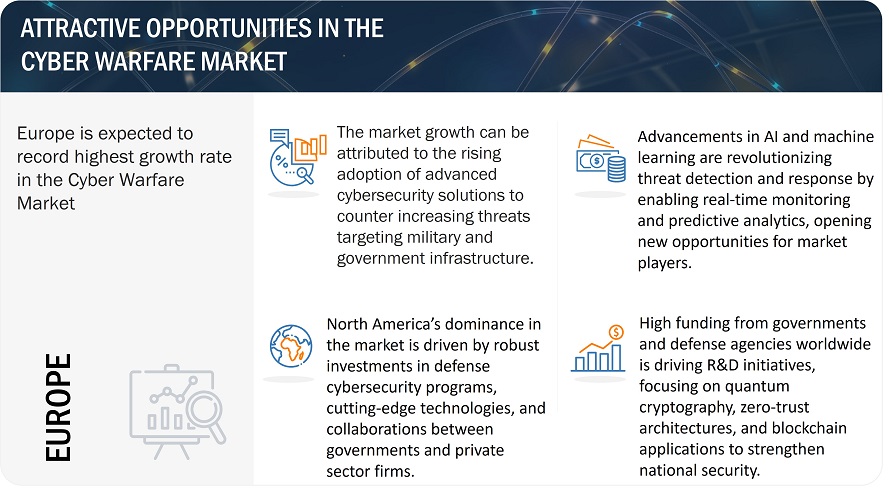
ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES IN THE CYBER WARFARE MARKET
CYBER WARFARE MARKET DYNAMICS
DRIVER: - INCREASING ADOPTION OF CYBER DEFENSE SOLUTIONS BY MILITARIES
As threats become more complex, be it state-sponsored attacks, ransomware, or espionage targeting critical infrastructure and classified systems, militaries all over the world are shifting towards cyber defense solutions. The growing complexity of APTs, zero-day vulnerabilities, and AI weaponized has made it pretty much necessary to have strong cyber defenses in place so that one can ensure one's operational readiness and national security. In return, governments have increased their cybersecurity defense budget massively. For example, the United States has improved its capacity to defend Department of Defense systems, while the European Defense Fund has inspired innovation in military cybersecurity for member states. Such investments point toward the fact that military strategies now consider changing threats and are prioritizing cybersecurity.
RESTRAINTS: HIGH COSTS AND INTEGRATION COMPLEXITIES
Among the military forces, some of the main challenges they face in regard to these cyber defense solutions include lack of affordability and problems with complex integration. Most of the modern cybersecurity technology, including AI-driven detection systems, encryption mechanisms, and real-time response tools, requires huge investment costs. Moreover, to remain one step ahead of the developing threats, one requires substantial resources for research, development, and personnel training for continuous maintenance and updates. The integration front is the most significant area where most militaries face difficulties in integrating new cyber defense technologies into the existing defense infrastructure. Most defense systems are either outdated or fragmented, and hence it is difficult to integrate modern cyber defense tools seamlessly. Complexity is also added by the issue of compatibility between different systems, legacy software, and hardware and the requirement for interoperability across various military branches. These systems must be tested and updated constantly in order to stay effective in this shifting cyber threat environment, a high resource and expertise-intensive activity.
OPPORTUNITY: - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND MACHINE LEARNING IN CYBER THREAT DETECTION
Integration of AI and ML with cyber threat detection will be a revolution in military cyber defense. The big data processing improves predictions and analyses significantly. They are able to recognize pattern changes in network traffic and user behavior, and sometimes even system activities that signify possible anomalies in cyberattacks. This predictive ability will allow military forces to prepare for threats and threats to develop before they materialize, thereby changing the nature of defense strategies from reactive to proactive. In addition, AI and ML will allow response in real time by automating countermeasures that would involve isolating compromised systems or initiating defensive action without requiring human intervention. Such a swift response time is very critical for an organization to contain probable damage from sophisticated attacks, like APTs, and zero-day vulnerabilities. In that regard, its guarantee of learning and evolving as new threats emerge allows its defense system in military organizations to stay effective. Their introduction would enhance its very much cyber resilience of a military organization, placing them way ahead of their rival.
CHALLENGE: - EVOLVING NATURE OF CYBER THREATS
Possibly the biggest challenge that military cyber defense faces is the nature that continues to change in cyber threats. Cyber threats have evolved to change from simple and unsophisticated scale into a much more complicated and sophisticated scale of adversaries using advanced tactics, techniques, and procedures. Military defense systems should continue to innovate to accommodate the high-speed-changing nature of such threats. Such an environment makes it very difficult for defense organizations to outwit the cyber adversaries because these adversaries usually challenge them to respond in real time to new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. This makes the traditional reliance on rules set by preset policies or static defensive tactics less effective most times because it can evade any classic security mechanism in place, and hence the defense needs constant revolution with improvements updated frequently in light of protecting the highly-sensitive networks, infrastructures, and sensitive information. This rapid pace of change also mounts heavy pressure on defense organizations to continually invest in research and development and train the latest cybersecurity methods. The call to continually innovate with regards to these evolving threats creates resources strain and may lead into an attitude of reaction rather than defending actively. As such, catching ahead of increasingly sophisticated adversaries becomes very much a challenge for military cyber defense systems.

1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
1.3 MARKET SCOPE
1.3.1 REGIONAL SCOPE
1.3.2 YEARS CONSIDERED FOR THE STUDY
1.4 CURRENCY
1.5 MARKET STAKEHOLDERS
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 RESEARCH DATA
2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
2.2.1 MARKET DEFINITION & SCOPE
2.2.2 SEGMENTS AND SUBSEGMENTS
2.3 RESEARCH APPROACH & METHODOLOGY
2.3.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
2.3.2 CYBER WARFARE MARKET FOR VERTICALS
2.3.3 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
2.4 TRIANGULATION & VALIDATION
2.4.1 TRIANGULATION THROUGH PRIMARY AND SECONDARY RESEARCH
2.5 GROWTH RATE ASSUMPTIONS
2.6 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
2.7 RISK ASSESSMENT
2.8 LIMITATIONS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
5.1 INTRODUCTION
5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
5.2.1 DRIVERS
5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
5.2.4 CHALLENGES
5.3 TRENDS AND DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
5.4 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
5.5 INDICATIVE PRICING
5.6 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
5.7 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2024–2025
5.8 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
5.9 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
5.10 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
5.11 IMPACT OF AI
5.12 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
5.13 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
6 INDUSTRY TRENDS
6.1 INTRODUCTION
6.2 EMERGING TRENDS
6.3 TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP
6.4 IMPACT OF MEGATRENDS
7 CYBER WARFARE MARKET, BY END USER
7.1 INTRODUCTION
7.2 LAND
7.3 NAVAL
7.4 AIRBORNE
7.5 SPACE
8 CYBER WARFARE MARKET, BY APPLICATION
8.1 INTRODUCTION
8.2 CYBER DEFENSE
8.2.1 NETWORK SECURITY
8.2.2 ENDPOINT SECURITY
8.2.3 CLOUD SECURITY
8.2.4 APPLICATION SECURITY
8.2.5 CONTENT SECURITY
8.2.6 INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEM (ICS) SECURITY
8.3 CYBER RESILIENCE
8.3.1 DETECTION AND RESPONSE
8.3.2 RECOVERY
9 CYBER WARFARE MARKET, BY SOLUTION
9.1 INTRODUCTION
9.2 THREAT INTELLIGENCE
9.2.1 THREAT MONITORING
9.2.2 THREAT DETECTION AND RESPONSE
9.3 DATA PROTECTION
9.3.1 DATA ENCRYPTION
9.3.2 DATA MASKING
9.4 IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT
9.4.1 SINGLE SIGN-ON
9.4.2 MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
9.5 MANAGED SECURITY SOLUTION
9.5.1 LOG MANAGEMENT
9.5.2 INCIDENT RESPONSE
9.6 SECURITY AND VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT
9.6.1 SECURITY OPERATIONS CENTER (SOC) AS A SERVICE
9.6.2 MANAGED DETECTION AND RESPONSE (MDR)
9.7 RESILIENCE SOLUTION
9.7.1 DISASTER RECOVERY
9.7.2 BUSINESS CONTINUITY PLANNING
9.7.3 INCIDENT RESPONSE AND RECOVERY
9.7.4 BACKUP AND RESTORE SOLUTIONS
10 CYBER WARFARE MARKET, BY REGION
10.1 INTRODUCTION
10.2 NORTH AMERICA
10.2.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR NORTH AMERICA
10.2.2 US
10.2.3 CANADA
10.3 EUROPE
10.3.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR EUROPE
10.3.2 UK
10.3.3 GERMANY
10.3.4 FRANCE
10.3.5 REST OF EUROPE
10.4 ASIA PACIFIC
10.4.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR ASIA PACIFIC
10.4.2 INDIA
10.4.3 JAPAN
10.4.4 AUSTRALIA
10.4.5 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
10.5 MIDDLE EAST
10.5.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR MIDDLE EAST
10.5.2 GCC COUNTRIES
10.5.2.1 UAE
10.5.2.2 SAUDI ARABIA
10.5.3 ISRAEL
10.6 REST OF THE WORLD
10.6.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR REST OF THE WORLD
10.6.2 LATIN AMERICA
10.6.2.1 BRAZIL
10.6.2.2 MEXICO
10.6.3 AFRICA
10.6.3.1 SOUTH AFRICA
11 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
11.1 INTRODUCTION
11.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/ RIGHT TO WIN
11.2 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS OF LEADING PLAYERS, 2023
11.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS 2019–2023
11.4 BRAND/ PRODUCT COMPARISON
11.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
11.6 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
11.6.1 STARS
11.6.2 EMERGING LEADERS
11.6.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
11.6.4 PARTICIPANTS
11.6.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT, KEY PLAYERS, 2024
11.6.5.1 COMPANY FOOTPRINT
11.6.5.2 REGION FOOTPRINT
11.6.5.3 DOMAIN FOOTPRINT
11.6.5.4 VERTICAL FOOTPRINT
11.6.5.5 SYSTEM FOOTPRINT
11.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
11.7.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
11.7.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
11.7.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
11.7.4 STARTING BLOCKS
11.7.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
11.7.5.1 DETAILED LIST OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
11.7.5.2 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
11.8 BRAND/ PRODUCT COMPARISON
11.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
11.8.1 LATEST DEVELOPMENTS
12 COMPANY PROFILES
12.1 INTRODUCTION
12.2 KEY PLAYERS
12.2.1 LOCKHEED MARTIN CORPORATION
12.2.2 RAYTHEON TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
12.2.3 NORTHROP GRUMMAN CORPORATION
12.2.4 BAE SYSTEMS
12.2.5 GENERAL DYNAMICS CORPORATION
12.2.6 BOOZ ALLEN HAMILTON.
12.2.7 CROWDSTRIKE
12.2.8 CISCO SYSTEMS
12.2.9 PALO ALTO NETWORKS
12.2.10 FORTINET
12.2.11 LEONARDO SPA
12.2.12 LEIDOS
12.2.13 IBM
12.2.14 CAIC
12.2.15 THALES GROUP
12.2.16 ELBIT SYSTEM
12.2.17 L3HARRIS TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
12 APPENDIX
12.1 DISCUSSION GUIDE
12.2 KNOWLEDGE STORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS’ SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
12.3 INTRODUCING RT: REAL-TIME MARKET INTELLIGENCE
12.4 AVAILABLE CUSTOMIZATION
12.5 RELATED REPORTS
12.6 AUTHOR DETAILS
Exhaustive secondary research was conducted to gather information on the cyber warfare market, its adjacent markets, and its parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Demand-side analyses were carried out to estimate the overall size of the market. Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate the complete market size. Then, the size of different segments and subsegments was estimated through market breakdown combined with data triangulation.
Secondary Research
In the secondary research process, various secondary sources, such as D&B Hoovers, Bloomberg, BusinessWeek, and different magazines were referred to identify and collect information for this study. Secondary sources also included annual reports, press releases & investor presentations of companies, certified publications, articles by recognized authors, and component research papers.
Primary Research
Extensive primary research was conducted after acquiring information regarding the cyber warfare market scenario through secondary research. Primary research also helped in understanding the various trends related to end users, solutions, applications, and regions. Stakeholders from the demand side include cyber solution providers, manufacturing companies, and the defense industry, who are willing to adopt cyber warfare by participating in various trials. These interviews were conducted to gather insights such as market statistics, data on revenue collected from the products and services, market breakdowns, market size estimations, market size forecasting, and data triangulation. These interviews also helped analyze the end user, solution, and market application for five key regions.
Market Size Estimation
Both, the top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the total size of the cyber warfare Market. These methods were also used extensively to estimate the size of various subsegments in the market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following:
- The key players in the industry and markets were identified through extensive secondary research.
- The industry’s supply chain and market size, in terms of value, were determined through primary and secondary research processes.
- All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources.
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size from the market size estimation process, the total market has been split into several segments and subsegments. To complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for market segments and subsegments, the data triangulation procedure has been implemented, wherever applicable. The data has been triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides. Along with this, the market size has been validated using both top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, segment, and forecast the size of the cyber warfare market based on end user, solution, application, and Region
- To forecast the size of different segments of the market with respect to five key regions, namely, North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Rest of the World, along with their key countries
- To identify and analyze the key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing the growth of the market
- To identify technology trends currently prevailing in the Cyber Warfare Market
- To analyze micromarkets with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and their contribution to the overall market
- To analyze opportunities in the market for stakeholders by identifying the key market trends
- To profile the leading market players and comprehensively analyze their market share and core competencies
- To analyze the degree of competition in the market by identifying the key growth strategies, such as acquisitions, new product launches, contracts, and partnerships, adopted by the leading market players
- To identify detailed financial positions, key products, and unique selling points of the leading companies in the market
- To provide a detailed competitive landscape of the market, along with a ranking analysis, market share analysis, and revenue analysis of the key players
Scope Of The Report
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Market size available for years |
2020–2029 |
|
Base year considered |
2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024-2029 |
|
Forecast units |
Value (USD Million) |
|
Segments covered |
By End User, By Solution, By Application, and By Region |
|
Geographies covered |
North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, the Middle East, and Rest of the World |
|
Companies covered |
BAE Systems (UK), Northrop Grumman Corporation (US), Lockheed Martin Corporation (US), Cisco Systems (US), Booz Allen Hamilton (US) Crowdstrike (US), IBM (US) and among others |
The study categorizes the Cyber Warfare Market based on segment like Solution, End User, Application, and Region
-
By End User
- Land
- Naval
- Airborne
- Space
-
By Solution
-
Threat Intelligence
- Threat Monitoring
- Threat Detection and Response
-
Data Protection
- Data Encryption
- Data Masking
-
Identity and Access Management
- Single Sign-On
- Multi-Factor Authentication
-
Managed Security Solution
- Log Management
- Incident Response
-
Security and Vulnerability Management
- Security Operations Center (SOC) as a Service
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
-
Resilience Solution
- Disaster Recovery
- Business Continuity Planning
- Incident Response and Recovery
- Backup and Restore Solutions
-
Threat Intelligence
-
By Application
-
Cyber Defense
- Network Security
- Endpoint Security
- Cloud Security
- Application Security
- Content Security
- Industrial Control System (ICS) Security
-
Cyber Resilience
- Detection and Response
- Recoverymeo
-
Cyber Defense
-
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- Rest of the World















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Cyber Warfare Market