Agricultural Enzymes Market by Type (Phosphatases, Dehydrogenases, Sulfatases), Product Type (Fertility Products, Growth Enhancing Products), Crop Type (Cereals & Grains, Oilseeds & Pulses, Turf & Ornamentals), and Region - Global Forecast to 2022
MarketsandMarkets forecasts the agricultural enzymes market to grow from USD 279.2 million in 2017 to USD 474.7 million by 2022, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.2% during the forecast period. The major factors that are expected to be driving the inclination toward agro-biologicals due to rise in prices of agro-chemicals, growth in organic farming and demand for organic food, and increase in production yield from limited arable land. The objective of the report is to define, describe, and forecast the agricultural enzymes market size based on type, crop type, product type, and region
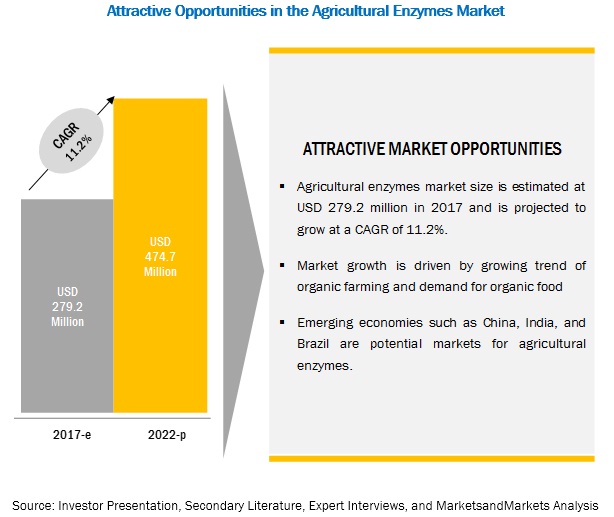
By type, the phosphatases segment is expected to grow at the highest growth rate during the forecast period
Among the types segment, the phosphatases segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. Phosphatases enzymes helps in catalyzing hydrolyses of esters and anhydrides of phosphoric acid, apart from being good indicators of soil fertility. They also place a key role in soil system; the ability to solubilize soil mineral elements by these phosphomonoesteraces is expected to be higher in biologically managed systems, because of a higher quantity of organic carbon found in those systems. There have been few studies examining the influence of management options in the ecosystem on phosphatases activity in soil where most crops are grown. Such factors drive the phosphatases segment of the agricultural enzymes market.
By crop type, the cereals & grains segment to record the largest market share during the forecast period
The cereals & grains crop type recorded largest market share in the 2016. Rice is the most widely consumed staple food for a large part of the global human population, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. Globally, rice is the second most widely produced grain, after corn. Asian countries accounted for about 90.5% of the global rice production in 2015. The climate in the Asia-Pacific region is suitable for the cultivation of cereals & grains. Cereal consumption in the Asia-Pacific region varies in accordance with the respective geographic and climatic conditions. Urbanization is one of the factors driving the demand for cereals & grains owing to different lifestyles, calorie requirements, increase in income, and food requirements. Agricultural enzymes are used for most cereal crops to enhance the yield as they fertilize the soil and enhance plant growth. As cereals are grown in most countries, the global demand for agricultural enzymes is also projected to grow.
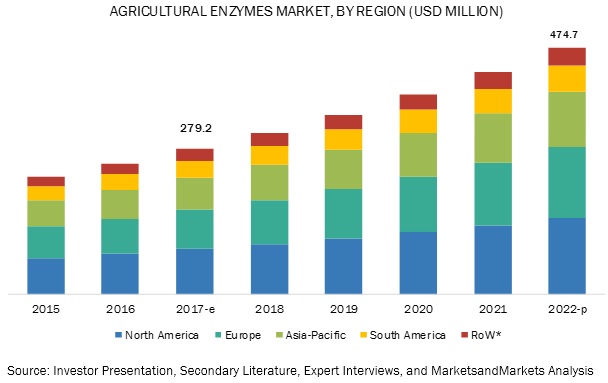
North America to account for the largest market size during the forecast period.
North America is expected to hold the largest market size in the agricultural enzymes market during the forecast period, followed by the Europe region. The highest market share of North America is due to the increasing environmental concerns, awareness about agricultural biotechnology, and application of advance farming technologies are driving the growth in the region. The farmers in North America are still producing healthier crops with higher yield, where enzymes act as agriculture enhancers. Prominent players such as Monsanto Company (US), Stoller USA Inc. (US), BioWorks, Inc. (US), and E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company (US) are involved in the North American agricultural enzymes market. The US is largely engaged in the agricultural industry, with stringent rules and regulations in place. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, certain guidelines have been laid down for the importation of microbe-produced materials. Moreover, these guidelines apply to import and export various materials, which includes enzymes, proteins, and extracts. This drives the agricultural enzymes market in the region.
Market Dynamics
Inclination Towards Agro-Biological
In order to meet the rising demand for food, resulting from the increasing global population, mineral & chemical fertilizers and pesticides have been used extensively to increase crop yield from arable land. Major fertilizer prices have seen declining trend over the years (2012 to 2016) due to the fall in overall agricultural commodity prices across the world alone with the fall in feed stock (especially urea feed stock) prices. On the other hand, regulatory challenges along with agriculture supply chain stakeholder’s inclination towards the use of eco-friendly and cost-effective alternatives such as bio-fertilizers, bio-stimulants, and micro-organisms in farm practices gaining higher popularity, which is projected weigh on fertilizers consumption.
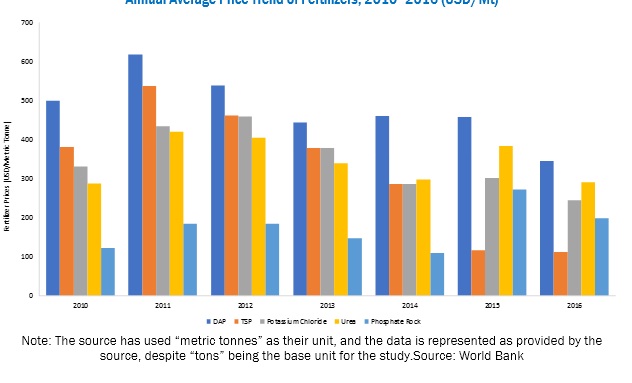
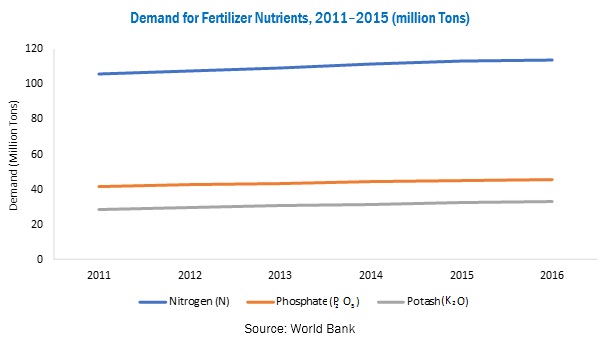
Due to a significant rise in fertilizer prices, farmers have started switching to using agricultural biologicals such as biofertilizers, biopesticides, and bio-enzymes. Agricultural biologicals in the form of biopesticides and biofertilizers are much cheaper than chemical fertilizers, owing to which they are preferred by growers. Agricultural enzymes, when mixed with fertilizers, also result in increased soil fertility and hence higher yield. According to a study conducted by the Crop Science Society of the Philippines, the performance of microbial enzymes in combination with different levels of soil-applied inorganic fertilizer applications varied with seasons and treatments; hence, the outcome in terms of yield, plant growth, and soil fertility may differ. Its application improved soil fertility and yield through enhanced plant growth. The research also concluded that the application of agricultural enzymes could be a suitable alternative to reduce the amount of soil-applied fertilizers by as much as 50%, and in turn reduce the overall production cost without giving up the economic yield.
Adoption of Modern Farming Practices to Mitigate Costs
Modern agricultural practices are seen as synchronization between access to resources, technology, management, investment, markets, and supportive government policies. Modern agriculture also focuses on the following:
- Development and maintenance of soil fertility through the specific provision of nutrients when they are depleted
- Machine power and technology to create soil conditions necessary to promote plant growth with minimal disturbance and minimal soil loss
- Use of improved genetics for crops and livestock to enhance yields, quality, and reliability
Plant growth and crop yields are primary indicators of productivity, which reflect both natural factors- including soil fertility, growing season length and temperature, rainfall amounts and reliability or access to irrigation-and technology in the form of genetics, fertilizer, machinery, management practices, crop protection, and other inputs. Farmers are increasingly becoming aware of modern farming techniques. There is an inclination toward usage of products that are economic, environmental friendly, and safe for humans. Agricultural enzymes fulfill these basic requirements of modern farming for higher yields. Agricultural enzyme products can be used for plant growth, soil fertility, and microbe control.
Farmers reluctant to adopt microbe-derived products
Farmers are reluctant to adopt microbe-derived products due to various reasons. Despite several successful products, farmers still have concerns about the performance of microbials. Moreover, farmers are accustomed to chemical pesticides and are reluctant to change this practice. The storage of microbial products is also a concern. Overall, the awareness about microbial products among farmers is low. Moreover, since different chemical pesticides have different application procedures, farmers are unaware of the benefits of microbial products, which ultimately prevent their adoption. Companies would need to invest significantly in developing marketing programs, educating masses, and conducting field trials to improve farmers’ perception about microbial products.
Scope of the Report
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Market size available for years |
2016–2022 |
|
Base year considered |
2016 |
|
Forecast period |
2017–2022 |
|
Forecast units |
Million (USD) |
|
Segments covered |
Type (phosphatases, dehydrogenases, proteases, sulfatases, and others), Crop type (cereals & grains, fruits & vegetables, oilseeds & pulses, turfs & ornamentals, and others), product type (soil fertility products and growth enhancing products), and Region |
|
Geographies covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and Row |
|
Companies covered |
Novozymes A/S, Syngenta AG, BASF, DuPont, DSM, Deepak Fertilisers, Bayer AG, Monsanto, American Biosystem, Aries Agro Limited, and BioResource International. |
The research report categorizes the agricultural enzymes to forecast the revenues and analyze the trends in each of the following sub-segments:
The Agricultural Enzymes Market, by Type:
- Phosphatases
- Dehydrogenases
- Proteases
- Sulfatases
- Others
The Agricultural Enzymes Market, by Crop Type:
- Cereals & grains
- Fruits & vegetables
- Oilseeds & pulses
- Turfs & ornamentals
- Others
The Agricultural Enzymes Market, by Product Type:
- Soil fertility products
- Growth enhancing products
The Agricultural Enzymes Market, by Region:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- RoW
Key Market Players
Novozymes A/S, Syngenta AG, BASF, DuPont, DSM, Bayer AG, Monsanto, Deepak Fertilisers, Aries Agro Limited, and BioResource International, which are focusing on expanding their market base in the agricultural enzymes market. This is successfully achieved with the assistance of numerous market strategies adopted by these companies, which includes mergers & acquisitions, new product launches, agreements, partnerships, collaborations, expansions, regulatory approvals and other strategies.
Recent Developments
- In February 2017, Novozymes A/S (Denmark) launched advanced enzymes Spirizyme T a suite of glucoamylase enzymes with trehalase. It also helps in enhancing the yields in plants.
- In January 2017, Agrinos AS (Norway) announced a new distribution partnership with Van Diest Supply Company based in Webster City, Iowa. This partnership will offer crop solution to growers and retailers throughout Midwest area of U.S. to increase biostimulant nutrition product lines for plant and soil health.
- In January 2017, Monsanto and Novozymes A/S (Denmark) collaborated to form the BioAg Alliance. This alliance developed a new product named Acceleron B-300 SAT, which improves and increases the nutrient uptake to the plants.
- In April 2017, Koninklijke DSM N.V. opened a new biotechnology center in Delft, Netherlands. This expansion would increase the research and development activities in various applications such as biotechnology-based materials and nutrition.
- In March 2017, DuPont signed an agreement with FMC Corporation (U.S.) (NYSE: FMC) to divest a portion of DuPont’s Crop Protection business, including certain research and development capabilities, as well as to acquire substantially all of FMC’s Health & Nutrition business.
- In July 2016, BioWorks, Inc. (U.S.) launched a new product named Mycotrol ESO. It can be used in greenhouses & nurseries and on turf & vegetables.
Critical questions the report answers:
- Where will all these developments take the industry in the long term?
- What are the upcoming trends for the agricultural enzymes market?
- Which segment provides the most opportunity for growth?
- Who are the leading vendors operating in this market?
- What are the opportunities for new market entrants?
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst

Table of Contents
1. Introduction
1.1 Objectives of the Study
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Market Covered
1.3.2 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Stakeholders
1.7 Limitations
1.8 Inclusions & Exclusions
2. Research Methodology
2.1 Research Data
2.1.1 Secondary Data
2.1.1.1 Key Data from Secondary Sources
2.1.2 Primary Data
2.1.2.1 Key Data from Primary Sources
2.1.2.2 Breakdown of Primaries
2.2 Market Size Estimation
2.2.1 Bottom-Up Approach
2.2.2 Top-Down Approach
2.3 Market Breakdown & Data Triangulation
2.4 Research Assumptions & Limitations
3. Executive Summary
4. Premium Insights
4.1 Attractive Opportunities in Agricultural Enzymes Market
4.2 Phosphatases: Leading Segment for Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Type
4.3 Asia-Pacific: Fastest-Growing Agricultural Enzymes Market
4.4 Spain to Grow at Highest CAGR in Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Country (2017–2022)
4.5 Life Cycle Analysis, By Region
5. Market Overview
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Macro Indicators
5.2.1 Increase in Organic Farmland
5.2.2 Growth of the Fertilizer Industry
5.2.3 Growth in Population and Decrease in Arable Land
5.3 Market Dynamics
5.3.1 Drivers
5.3.1.1 Inclination Toward Agro-Biologicals
5.3.1.2 Increase in Trend of Organic Farming and Demand for Organic Food
5.3.1.3 Increase in Production Yield from Limited Arable Land
5.3.2 Restraints
5.3.2.1 Stringent International Regulations Related to Biological Products
5.3.3 Opportunities
5.3.3.1 Adoption of Modern Farming Practices to Mitigate Costs
5.3.3.2 Future Demand for Soil Enzymes Due to Soil Pollution
5.3.4 Challenges
5.3.4.1 Farmers Reluctant to Adopt Microbe-Derived Products
5.3.4.2 High R&D Cost and Extensive Duration for Patent Approval
5.4 Supply/Value Chain
5.5 Connected Market
5.6 Regulatory Framework
6. Industry Trends
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Value Chain Analysis
6.3 Supply Chain Analysis
6.4 International Regulatory Frame Work
6.4.1 Amendments in Enzyme Safety & Quality Assurance Regulations
6.5 International Patent Analysis
6.5.1 Soil Enzymes: Trends in International Patent Filing, 1931–2016
6.6 YC – YCC Shift
7. Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Type
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Phosphatases
7.2.1 The Ability to Solubilize Soil Mineral Elements By These Phosphomonoesteraces Is Expected To Be Higher In Biologically Managed Systems
7.3 Dehydrogenases
7.3.1 Dehydrogenases are Known to Oxidize Soil Organic Matter By Transferring Protons And Electrons From Substrates to Acceptors
7.4 Proteases
7.4.1 Proteases in Soil Play a Significant Role in Nitrogen Mineralization
7.5 Sulfatases
7.5.1 The Sulfate for Plant Nutrition is Provided By Microbial Turnover of Organically-Bound Sulfur
7.6 Ureases
7.6.1 Soil Urease Originates Mainly From Plants and Microorganisms, Found As Both Intra- And Extra-Cellular Enzymes
7.7 Others* (Beta-Glucosidase and Cellulases)
8. Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Crop Type
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Cereals & Grains
8.2.1 Cereals are Grown on Massive Scales Under Almost All Climatic Conditions
8.3 Oilseeds & Pulses
8.3.1 Soybean is an Important Crop Which Provides Oil and Protein; It Is Widely Grown For Its Edible Bean
8.4 Fruits & Vegetables
8.4.1 The Ripening and Growth of Fruits Are Catalyzed With the Help of Agricultural Enzymes
8.5 Turfs & Ornamentals
8.5.1 Rapid Promotion of Tourism and Increasing Area of Land Under Golf Courses and Gardens
8.6 Others* (Plantation, Herbs, and Spices)
9. Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Product Type
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Soil Fertility Products
9.2.1 Soil Fertility Refers to the Crop Yield Potential and it is Vital for Increasing Yields And Profit for Farmers
9.3 Plant Growth Enhancing Products
9.3.1 Plant Growth Enhancers Have Been Benefiting the Farming Community and the Agro-Processing Industry
10. Agricultural Enzymes Market, By Region
10.1 Introduction
10.2 North America
10.2.1 US
10.2.1.1 Guidelines Have Been Laid Down for the Importation of Microbe-Produced Materials
10.2.2 Canada
11.2.2.1 Increasing Preference for Organic Agriculture Among Canadian Farmers And Creating Opportunities
10.2.3 Mexico
10.2.3.1 Stringent Regulations Are Playing Role in the Market Growth for Agricultural Fertilizers
10.3 Europe
10.3.1 Germany
10.3.1.1 Higher Consumer, Government Policies, and Extensive R&D to Develop Effective Agricultural Enzymes by Developing New Strains
10.3.2 France
10.3.2.1 Cereals & Grains Specialty Generates Opportunities for Different Types Of Agricultural Enzymes In The French Market
10.3.3 UK
10.3.3.1 Increased Consumer Awareness About The Health Benefits Of Organic Food Is Driving The Market
10.3.4 Italy
10.3.4.1 Organic Farming is One of The Practices Supported By the European Union’s Rural Development Program in Italy
10.3.5 Spain
10.3.5.1 Rise in the Percentage of Organic Farming and Demand for Organic Products are Driving the Market
10.3.6 Russia
10.3.6.1 Awareness of Biotechnology Is One of the Major Factors Driving the Growth in This Market
10.3.7 Rest of Europe (Includes Rest of EU Countries, CIS and Non CIS Countries)
10.4 Asia-Pacific
10.4.1 China
10.4.1.1 Enzymes That Are Regulated In Soil Mainly Come From Plants And Microbes, And Play A Vital Role In The Nutrient Cycling Process
10.4.2 India
10.4.2.1 Strategic Initiative of Ministry Of Agriculture, Government of India, Has Laid Down Certain Guidelines
10.4.3 Japan
10.4.3.1 Soil Is Rich in Nutrients Helps in Improving Soil Structure and Soil Moisture Retention
10.4.4 Australia & New Zealand
10.4.4.1 The Favorable Foreign Investment Policies of the Government and the Push for Sustainable Agriculture
10.4.5 South Korea
10.4.5.1 Soil Enzymes Provide Enhanced Fertility, Along With the Controlled Availability of Microbes in the Soil
10.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific (Includes Philippines And Indonesia)
10.5 South America
10.5.1 Brazil
10.5.1.1 Soil, Microbial Biomass Plays a Vital Role in Nutrient Cycling, Plant Pathogen Suppression, And in Maintaining Soil Quality.
10.5.2 Argentina
10.5.2.1 Argentina is at the Forefront of the Introduction of Innovative Technologies to Its Farmers
10.5.3 Chile
10.5.3.1 Major Producer of Oilseeds, And Vegetables; Here, Cellulases Has A Very Important Application in Fruits
10.5.4 Rest of South America
10.6 Rest of World
10.6.1 Middle East
10.6.1.1 Environment Safety, Health Concern, and Socioeconomic Conditions Are Driving the Market Growth
10.6.2 Africa
10.6.2.1 Increasing Modern Plant Breeding Techniques to Enhance the Nutrient Uptake
11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Competitive Leadership Mapping
11.2.1 Visionary Leaders
11.2.2 Dynamic Differentiators
11.2.3 Innovators
11.2.4 Emerging Companies
11.3 Market Share Analysis
11.4 Competitive Scenario
11.4.1 Expansions
11.4.2 New Products Launches
11.4.3 Acquisitions
11.4.4 Agreements
12. Company Profiles
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Novozymes A/S
12.2.1 Business Overview
12.2.2 Company Scorecard
12.2.2.1 Product Offering
12.2.2.2 Business Strategies
12.2.3 Recent Developments
12.3 Syngenta AG
12.3.1 Business Overview
12.3.2 Company Scorecard
12.3.2.1 Product Offering
12.3.2.2 Business Strategies
12.3.3 Recent Developments
12.4 BASF SE
12.4.1 Business Overview
12.4.2 Company Scorecard
12.4.2.1 Product Offering
12.4.2.2 Business Strategies
12.4.3 Recent Developments
12.5 Dowdupont
12.5.1 Business Overview
12.5.2 Company Scorecard
12.5.2.1 Product Offering
12.5.2.2 Business Strategies
12.5.3 Recent Developments
12.6 DSM
12.6.1 Business Overview
12.6.2 Company Scorecard
12.6.2.1 Product Offering
12.6.2.2 Business Strategies
12.6.3 Recent Developments
12.7 Bioworks, Inc.
12.8 Agri Life
12.9 Bayer AG
12.10 Monsanto Company
12.12 Stollerusa
12.13 AB Enzymes
12.14 Deepak Fertilisers
12.15 Aries Agro Limited
12.16 Camson Bio Technologies Limited
12.17 Agrinos As
12.18 Lonza Group
12.19 Chr. Hansen
12.20 Bioresource International, Inc.
13. Appendix















Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Agricultural Enzymes Market