Zero Trust Security Market Size Share, Growth Analysis, By Offering (Solutions and Services), Application, Security type, Authentication Type, Vertical (Retail & E-commerce, Healthcare, Energy & Utilities) and Region - Global Industry Forecast to 2029
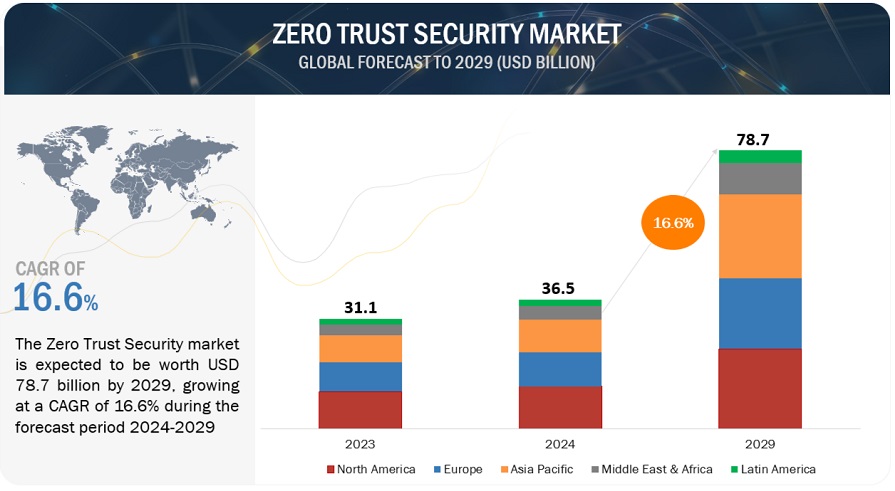
[330 Pages Report] The global Zero Trust Security Market is projected to grow from USD 36.5 billion in 2024 to USD 78.7 billion by 2029 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.6% during the forecast period. The zero trust security market is showing promising growth due to the rising threat of cyberattacks.
The zero trust security market is growing fast as cyber threats get more complex and companies move to remote work and cloud systems. Zero trust security’s main idea is never to trust; always check. That means every user and device must prove who they are before they can access anything, no matter where they are from. This approach has fallen in sight because of several reasons: more cyberattacks, more use of cloud tech, more people working from home, and stricter rules about data privacy. They primarily focus on combining zero trust with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and using AI and machine learning to boost security. Since hackers are coming up with new tricks, zero trust is becoming a must-have for companies to guard their sensitive info and systems in this digital world.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report

To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI ON ZERO TRUST SECURITY MARKET
Generative AI is causing a revolution in zero trust security providing several main benefits. It improves threat detection by examining huge data sets to identify anomalies, possible threats, and conventional approaches. Systems powered by AI can also automate responses to threats, which cuts down on human mistakes and response time. AI evaluates risk profiles to optimize security measures and resource distribution. It speeds up incident response by automating tasks and giving useful insights to security teams. Along with the advantages, AI also creates new attack possibilities, such as AI-created phishing attacks or adversarial AI. Generative AI shows great potential to boost zero trust security by enhancing threat detection, response, and risk assessment, although it requires careful thought about the possible risks and the creation of strong defenses against AI-based threats. As AI technology expands, it becomes essential for businesses to stay alert and flexible in their security plans.

ZERO TRUST SECURITY MARKET DYNAMICS
Driver: Rapid adoption of cloud and surge in digital transformation.
Organizations need advanced security for protection in complex IT environments; therefore, zero trust security becomes very important in protecting relevant data and avoiding losses. Traditional perimeter-based security no longer works in the wake of such aspects as remote work, mobile devices, and cloud computing that give blanket access once into the network. Zero trust security enforces strict access control and continuous authentication at all times so that users' access is thus verified and limited. It avoids the lateral movement of threats and offers better protection of critical data; therefore, its rise as a robust alternative has been witnessed. This means every request, whether user, device, or application request, must be continuously authenticated and allowed within the internal network. It reduces the chance of unauthorized access and the lateral movement of threats by making sure that only authenticated entities have access to important resources and data. As digital transformation and cloud adoption, together, result in enterprises facing a really complicated, networked IT environment for securing data and apps, establishing a strong, very advanced security solution to protect critical data and prevent losses becomes mandatory. As far as this respect is concerned, cloud computing and development in digital transformation have accelerated the demand for zero trust security solutions that reduce unauthorized threats and ensure access of key resources to only authorized persons. The increasing adoption of cloud environments and the current digital transformation act as drivers in the zero-trust security market. The "digital transformation"—that is, the process of integrating digital technologies into all facets of business operations—begets a much more complex and networked IT environment. This in effect means that businesses are rapidly deploying many devices, cloud-based applications, and networked systems that increase the attack surface for cyberattacks. The increased leverage of multi-cloud settings underscores a security plan designed to protect apps and their data across a number of cloud platforms. In that respect, zero trust security is implemented more successfully in businesses. Zero trust security follows the adage, "never trust, always verify".
Restraint: Complexity and costly implementation
The implementation of zero-trust security for any business, particularly for those with expansive and complicated network infrastructures, which can be quite a difficult and expensive procedure. Since it is complex and hard to understand and implement, it can contain potential mistakes in its implementation that may further endanger the security of the organization. It is also an expensive security approach that shall require the installation of new equipment and software and training of IT personnel. This may put certain organizations under a considerable financial burden. Moreover, this approach requires considerable changes in existing IT policies, procedures, and systems, which itself is a time- as well as a resource-consuming process. Furthermore, the upfront cost and continuous maintenance make some firms reluctant to adapt zero trust security solution at all. For instance, imposing zero-trust security creates problems in a multi-national organization with an extensive network architecture. The network is across multiple sites; underpinning it are a number of legacy systems that are very hard to integrate with modern zero-trust solutions. The cost in terms of redesigning the whole network and integration with legacy systems to include zero-trust security has resulted in the adoption process grinding to a halt.
Opportunity: Surge in awareness regarding zero trust security
The growing awareness regarding zero-trust security is creating huge opportunities for businesses in the cybersecurity sector. The zero-trust security designs its way to become the viable replacement for traditional methods under increasing cyber threats in terms of frequency and inadequacy. More education in this regard means a more potent market for the zero-trust security solution, ultimately leading to growing demands for related goods and services. It builds a very promising market for zero-trust security because now, organizations seek and look to invest in zero-trust security to further beef up the cybersecurity posture.
This increased level of awareness has precipitated openings for a good number of support services within the zero-trust security space. Cybersecurity consulting businesses will make hay by offering expert advice on how to correctly install and integrate such solutions for businesses that would like to do so successfully. As corporations crave to have their staff well-versed with the best practices and principles of zero-trust security, there is a corresponding surge in demand for educative material and training courses. The companies are also eying joint ventures and collaborations with other firms, including cloud service providers, toward the building of a uniform and all-inclusive security ecosystem. Hence, businesses are tactically positioning themselves to provide for these companies' changing security needs and benefit from increased demand for reliable and flexible security solutions as the awareness provided by these changing needs expands.
Challenges: Growth of shadow SaaS applications
Business-led IT or Shadow SaaS is what it is called when employees obtain and implement IT services without any sort of notification or approval from the IT Department. It is becoming more common for this phenomenon to happen today. Cloud storage and SaaS apps can be examples among many other IT services. The most important benefits of business-led IT are simplicity and speed of access to apps. Implementation into a zero-trust security framework itself, in the best-case scenario, will take weeks or months, killing the benefits brought about by efficiency and corporate agility. Employees
This can often mean that productivity-enhancing SaaS applications get bought directly by the would-be productive, bypassing the formal procurement process and the IT department—a challenge for zero-trust security. This thus implies that these rogue applications are a security threat since they are beyond the institution's security policy control and may uphold different security standards as other apps. An example is that shadow Saas applications may not be encrypted, patched rarely, or audited for vulnerabilities; they hence expose themselves to far greater degrees of cyber-attacks as a result.
Zero Trust Security Market Ecosystem
By vertical, the IT&ITeS segment is to account for a larger market size during the forecast period.
This can be attributed to the massive growth that the information technology and IT-enabled services industries have been registering in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific, hence becoming a most preferred target with its rapid growth and volume of sensitive employee and company data. Besides, cloud computing, IoT devices, and BYOD rules only add to the proliferation in the attack surface, which has grown multi-fold. The very critical communication infrastructure remains in the hands of telecom operators, who themselves become a target for sophisticated attacks, including ransomware and DDoS attacks, with an aim to put at risk sensitive data. The two major factors driving this trend are Z regulations and the sophistication of modern-day cyber-attacks. Zero Trust security solutions are protecting the world's infrastructure; it is one of the tools available for IT companies and IT service providers to effectively wage back in the face of growing cyber threats.
By Security Type, the Cloud Security segment is to account for a larger market size during the forecast period
Zero-trust security concepts are of growing importance in a fast-changing cybersecurity environment, particularly in the context of the cloud. Distributed apps and data in the adoption of cloud computing present a problem to organizations wishing to monitor access, usage of data, and security policy compliance. A variety of cloud security solutions have been developed following the paradigm of Zero Trust to help solve these issues. CASBs are mediators that provide close access control and constant monitoring of user activities in cloud applications. The proper and continuous assessment and hardening of cloud configurations are important means through which CSPM tools contribute to the reduction of vulnerabilities and the assurance of good security postures. CWPPs implement a model of workload protection for cloud-native applications that's based on "never trust, always verify.".
By Authentication Type, the Multi-factor Authentication to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period
Multi-factor authentication basically combines a few identifiers from people and from computers or software to verify one's identification. These can include passwords or PINs, passports, tokens, access cards, software certificates, biometric data, fingerprints, face recognition, and so on that constitute these identifiers. The development of multi-factor authentication has been the real backbone in identity verification and authentication. Some of the most popular MFA identifiers in use today are user passwords/PINs, cryptographic hardware security tokens, smartcards, software-based certificates, and a large group of techniques using biometric factors like retinal scans, fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and voice recognition. MFA forms a base component of the zero-trust security model since it creates a high-valued barrier to entry that will keep unauthorized users out of the system in case an attacker has managed to compromise one component. Since successful verification normally happens in a single session, MFA can effectively block attacks like persistence and lateral movement.
According to the PCI DSS rules, MFA solutions are a must for companies processing sensitive data, more so those within the sphere of payments. One major driving force behind the wide adoption of MFA across industries such as BFSI, government & defense, IT and telecom, healthcare, retail & eCommerce, energy & power, and manufacturing is the growing demand for robust identification and authentication techniques to protect sensitive information. Key players in zero-trust security develop highly advanced multi-factor authentication solutions by integrating state-of-the-art technologies, such as vein detection, thermal image identification, hand geometry, etc., which, in turn, would raise the market's further growth globally.
By region, North America will have the largest market size during the forecast period.

The North American market, including the US and Canada, is characterized by a high concentration of security vendors and a rise in cyberattacks. This sector may maintain a leading position in the zero trust security market for some time to come because of its early adoption of cutting-edge technologies. The increase in sophisticated cyberattacks is one of the key factors driving businesses to implement zero trust security solutions. The increasing usage of IoT, digital payments, cloud-based apps, and OT, as well as industries including banking, finance, government, and healthcare, the region is now more susceptible to cyberattacks. This was demonstrated in the January MailChimp attack, where hackers gained unauthorized access and affected a significant number of users by using social engineering techniques. These kinds of incidents emphasize how important it is to have a zero-trust policy, which may effectively stop escalations and restrict lateral movement within networks.
Key Market Players
Palo Alto Networks (US), VMware (US), Zscaler (US), Akamai (US), Microsoft (US), Cisco (US), IBM (US), Qnext (US), Citrix (US), Check Point (Isreal), Trellix (US), Forcepoint (US), CrowdStrike (US), Cloudflare (US), Fortinet (US), and Google (US) are some of the key players operating in the global Zero Trust Security market.

Want to explore hidden markets that can drive new revenue in Zero Trust Security Market?
Scope of the Report

Want to explore hidden markets that can drive new revenue in Zero Trust Security Market?
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size available for years |
2018–2029 |
|
Base year considered |
2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024–2029 |
|
Forecast units |
Value (USD Million/USD Billion) |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Geographies covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East Africa, and Latin America. |
|
Major Companies covered |
Major vendors in the global Zero Trust Security market include Palo Alto Networks (US), VMware (US), Zscaler (US), Akamai (US), Microsoft (US), Cisco (US), IBM (US), Qnext (US), Citrix (US), Check Point (Isreal), Trellix (US), Forcepoint (US), CrowdStrike (US), Cloudflare (US), Fortinet (US), and Google (US). |
The study categorizes the Zero Trust Security market by offering, application, security type, authentication type, vertical, and region.
By Offering
- Solutions
- Services
By Application
- Access Control/ Data Access Control
- API Security
- User Behaviour Analytics (UBA)
- Security Analytics
- Other Applications
By Security Type
- Network security
- Application Security
- Cloud Security
- Data security
- Endpoint security and IoT security
By Authentication Type
- Single-Factor Authentication
- Multi-Factor Authentication
Vertical
- Banking, Financial Services, And Insurance (BFSI)
- Government And Defense
- IT & ITES
- Healthcare
- Retail And E-commerce
- Energy And Utilities
- Other Verticals
Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
Recent Development
- In May 2024, Palo Alto Networks launched Prisma 3.0. Prisma SASE 3.0 extends Zero Trust to unmanaged devices, secures data with AI, and boosts application performance for partners and customers. Prisma SASE continues to deliver industry-leading SLAs for security processing and app performance. Prisma SASE 3.0 and its updated capabilities will be generally available in the coming months.
- In May 2024, Palo Alto Networks launched a host of new security solutions to help enterprises thwart AI-generated attacks and effectively secure AI-by-design. Leveraging Precision AI, the new proprietary innovation that combines the best of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) with the accessibility of Generative AI (GenAI) for real-time.
- In October 2021, VMware announced a range of security innovations, including zero trust architecture, ransomware protection, API security, and distributed workforce solutions, providing comprehensive and effective security for modern enterprises.
- In January 2024, Zscaler Zero Trust SASE, is a single-vendor SASE solution. The new platform is expected to use Zscaler Zero Trust AI to help organisations reduce cost and complexity while implementing Zero Trust security across users, devices, and workloads.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the definition of the ZeroTrust Security market?
The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in its current draft of standards for zero trust architecture, defines zero trust in the following manner: “Zero trust is a cybersecurity paradigm focused on resource protection and the premise that trust is never granted implicitly but must be continually evaluated.” Zero-trust security is, therefore, not only a product or an approach—it is a web of connected policies, practices, software, and hardware that create an entire zero-trust ecosystem.
What is the projected market value of the global Zero Trust Security market?
The global Zero Trust Security market is projected to grow from USD 36.5 billion in 2024 to USD 78.7 billion by 2029 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.6% during the forecast period.
Who are the key companies influencing the market growth of the Zero Trust Security market?
Palo Alto Networks (US), VMware (US), Zscaler (US), Akamai (US), Microsoft (US), Cisco (US), IBM (US), Qnext (US), Citrix (US), Check Point (Isreal), Trellix (US), Forcepoint (US), CrowdStrike (US), Cloudflare (US), Fortinet (US), and Google (US) are some of the key players operating in the global Zero Trust Security market.
What are some of the mandates for Zero Trust security?
Continuous verification is a core principle of Zero Trust Security that involves constantly evaluating and authorizing every access request based on real-time factors such as user identity, device security posture, and contextual information.
Which region is expected to show the highest CAGR in the Zero Trust Security market?
Asia Pacific is expected to account for the highest CAGR during the forecast period 2024-2029. .
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst

The market size of zero trust security was ascertained through a range of essential research efforts. A lot of secondary research was done to learn more about the sector. Primary research with industry professionals from all points of the value chain then confirmed these conclusions, hypotheses, and estimates. A variety of strategies, including top-down and bottom-up approaches, were used to estimate the total market size. The market sizes of the various segments and subsegments within the zero trust security market were then determined using market segmentation and data triangulation approaches.
Secondary Research
During the secondary research phase, various sources were looked into to gather information for the study. These secondary sources included annual reports, press releases, investor presentations from Zero Trust Security software and service providers, online forums, accredited publications and white papers. This secondary research was used to get insights into the industry supply chain, key players, market segmentation down to granular level, regional markets and notable developments from market and technology perspective. These findings were then validated through primary sources. Factors considered to estimate regional market size included government and technology initiatives, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rates, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) spend, recent market developments and a thorough analysis of major Operational Technology Security solution providers’ market position.
Primary Research
The comprehensive market engineering process employed a combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches, complemented by various data triangulation methods, to estimate accurately and forecast market trends for overall market segments and subsegments outlined in the report. The report accordingly compiled and presented key insights and information through accurate qualitative and quantitative analyses ran throughout the market engineering process.
After completing the market engineering process, which encloses calculations for market statistics, segmentation breakdowns, market size estimations, forecasts, and data triangulation, thorough primary research was conducted. This primary research gathered, verified, and validated critical numerical data and identified segmentation types, industry trends, and the competitive landscape within the Zero Trust Security market. The primary research was instrumental in elucidating fundamental market dynamics, Including drivers, restraints, opportunities, challenges, industry trends, and strategic initiatives market players adopt.
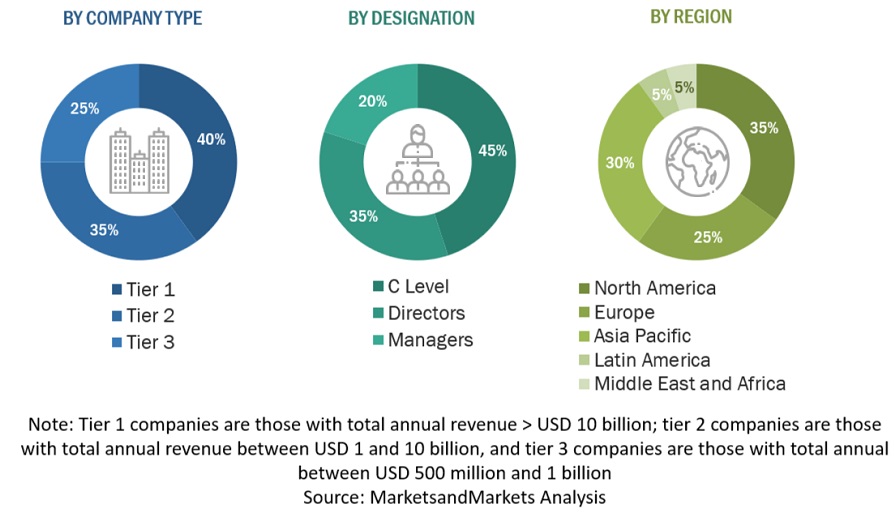
Following is the breakup of the primary study:
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both top-down and bottom-up methods were implemented to get an accurate picture of the global Zero Trust Security market's size. Also evaluated the sizes of different parts within this bigger market. This approach had several steps:First, Identifying the main players in the market through a lot of background reading. Then, looked at the revenue made in different Regions by the players. To do this, Have gone through reports and spoken to people in charge. Spent time looking at yearly and revenue reports from the top companies. Also had primary interviews with industry leaders like CEOs, VPs, directors, and marketing bosses to learn more. All the numbers about market splits and different parts came from reading reports. Re-ensured these numbers were Accurate by talking to Officials.
INFOGRAPHIC DEPICTING BOTTOM-UP AND TOP-DOWN APPROACHES

To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Data Triangulation
Following the determination of the overall market size using the market above size estimation methodologies, the market was segmented into distinct segments and subsegments. Data triangulation and market segmentation procedures were utilized, as needed, to complete the comprehensive market engineering process and ascertain the precise statistics for each market segment and subsegment. Data triangulation was achieved by analyzing various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides.
Market Definition
The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in its current draft of standards for zero trust architecture, defines zero trust in the following manner: “Zero trust is a cybersecurity paradigm focused on resource protection and the premise that trust is never granted implicitly but must be continually evaluated.” Zero trust security is, therefore, not only a product or an approach—it is a web of connected policies, practices, software, and hardware that create an entire zero-trust ecosystem.
According to CrowdStrike, zero trust is a security concept that requires all users, even those inside the organization’s enterprise network, to be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validating security configuration and posture before being granted or keeping access to applications and data.
Further, according to Akamai Technologies, zero trust is a network security model, based on a strict identity verification process. The framework dictates that only authenticated and authorized users and devices can access applications and data. At the same time, it protects those applications and users from advanced threats on the Internet”.
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, and forecast the Zero Trust Security market based on offering, application, security type, authentication type, vertical, and region.
- To forecast the market size of five central regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Middle East & Africa (MEA), and Latin America.
- To analyze the subsegments of the market concerning individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions to the overall market.
- To provide detailed information related to the primary factors (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges) influencing the growth of Zero Trust Security market.
- To analyze opportunities in the market for stakeholders by identifying high-growth segments of the Zero Trust Security market.
- To profile the key players of the Zero Trust Security market and comprehensively analyze their market size and core competencies.
- Track and analyze competitive developments, such as new product launches, mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, agreements, and collaborations in the global Zero Trust Security market.
Customization Options
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations based on company-specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
Geographic Analysis
- Further breakup of the Asia Pacific market into major countries.
- Further breakup of the North American market into major countries.
- Further breakup of the Latin American market into major countries.
- Further breakup of the Middle East African market into major countries
- Further breakup of the European market into major countries.
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to 5)




 Generating Response ...
Generating Response ...










Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Zero Trust Security Market